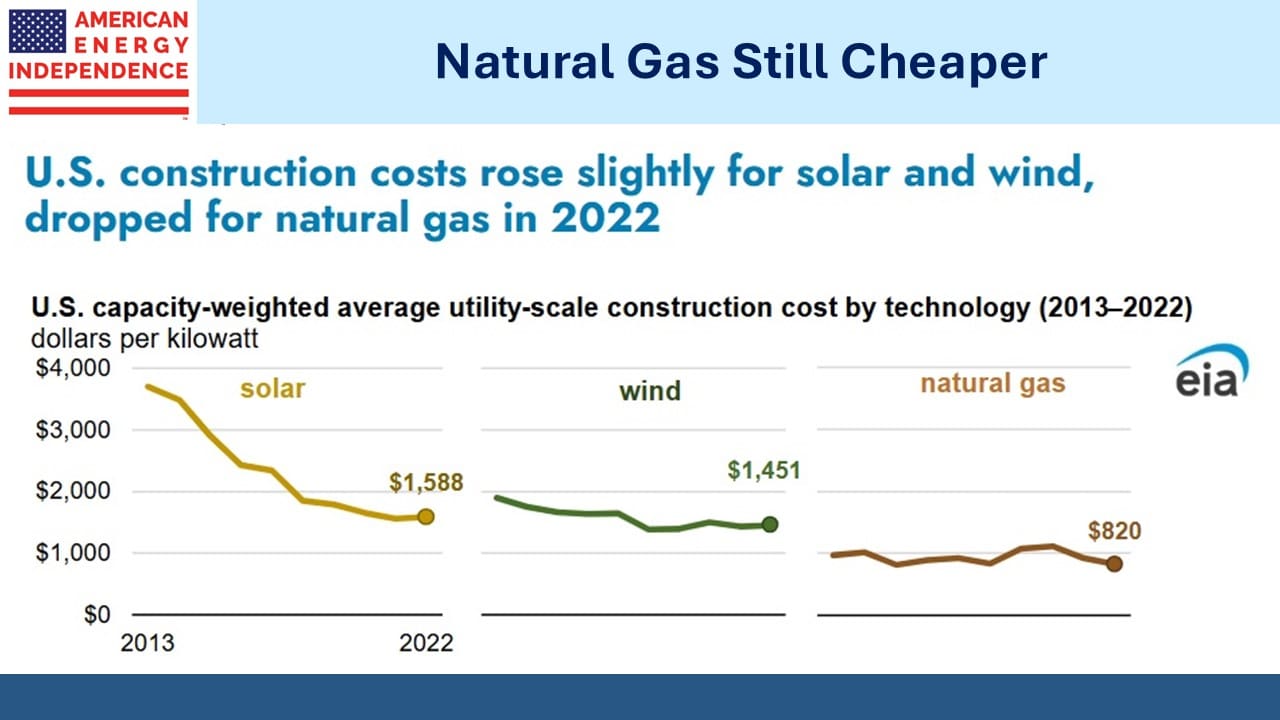
AI Demand Ramps Up

On Monday Energy Transfer announced the first Behind The Meter (BTM) agreement of the AI era. They’ll provide up to 450 Million Cubic Feet per Day of natural gas to a data center being built by CloudBurst Data Centers in central Texas.
This represents 0.45 Billion Cubic Feet per Day (BCF/D), almost 0.5% of US gas production and a staggeringly large amount for a single location.
As we noted recently (see Hyperscalers Plow Ahead), BTM arrangements don’t spread the cost of new power infrastructure across existing users. This avoids triggering a political backlash since data centers generate few jobs.
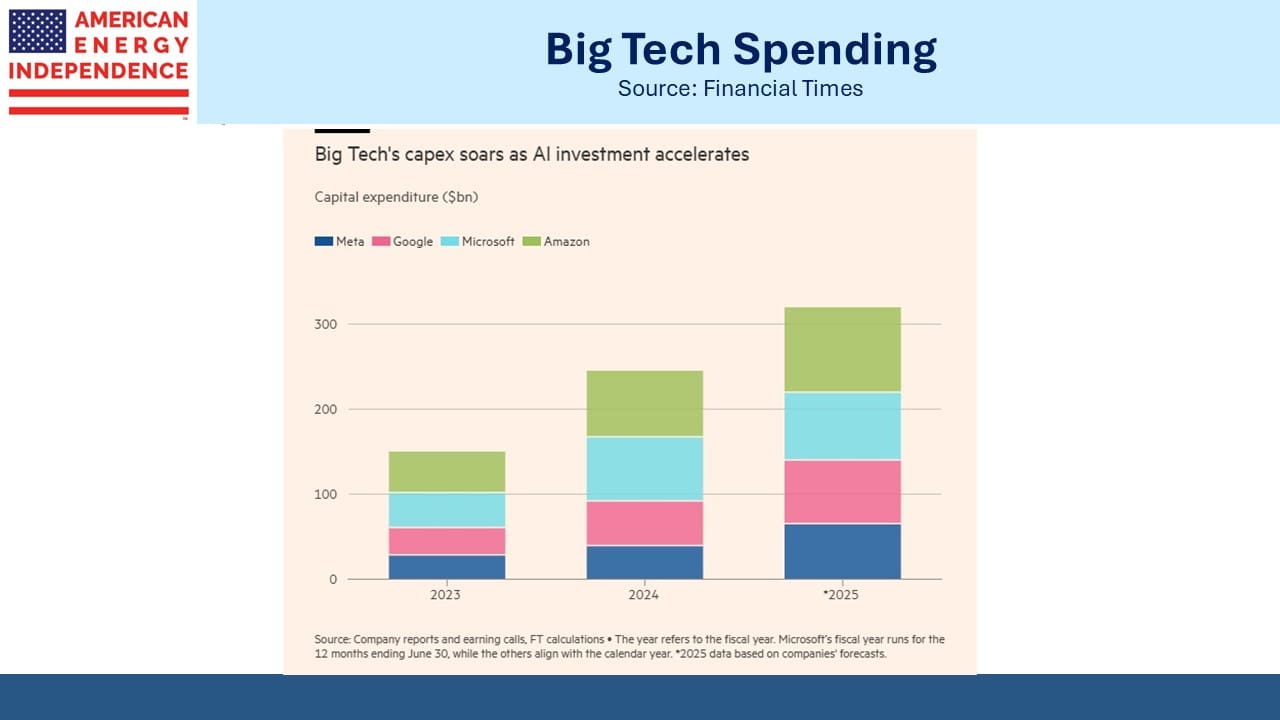
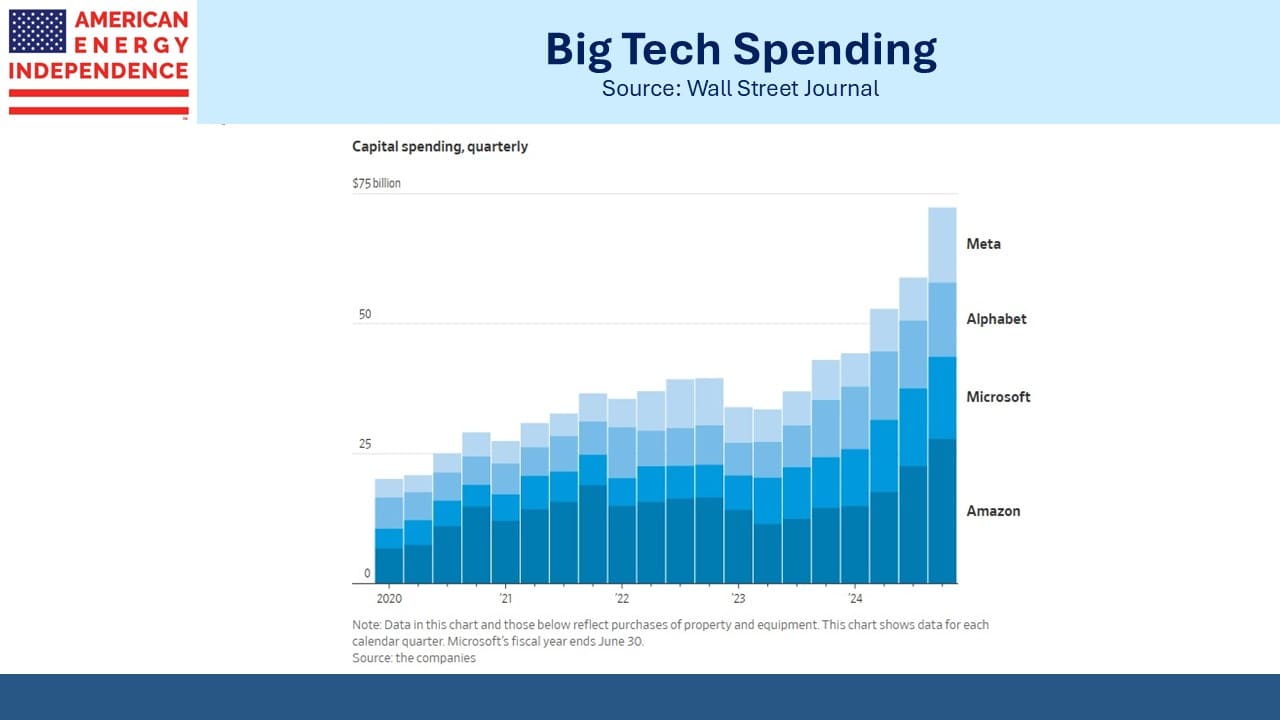
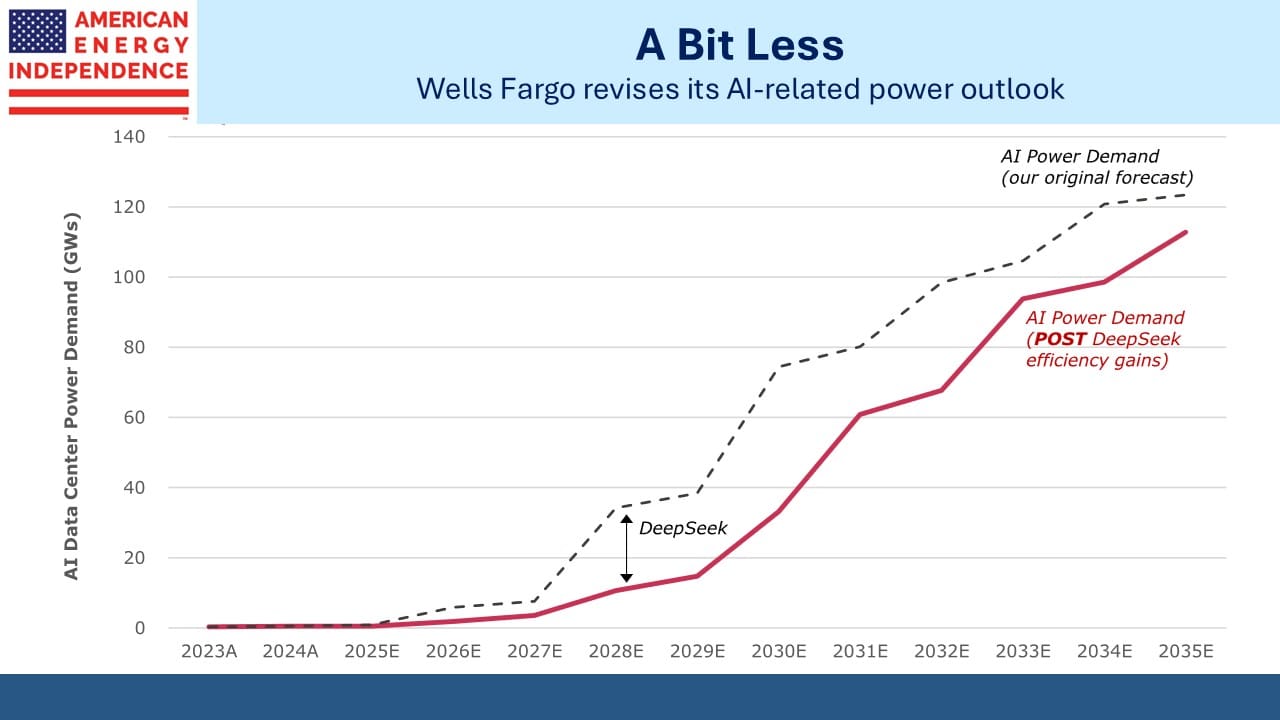
A couple of weeks ago DeepSeek cast doubt on the forecast increases in power demand that have helped boost natural gas infrastructure stocks (see Pipelines And The Jevons Paradox). Since then, companies such as Meta and Amazon have reaffirmed their capex budgets on data centers.
Morgan Stanley estimates that the first data centers to support the $500BN Stargate project that President Trump recently announced with require 0.66 BCF/D if fully supported with natural gas driven electricity.
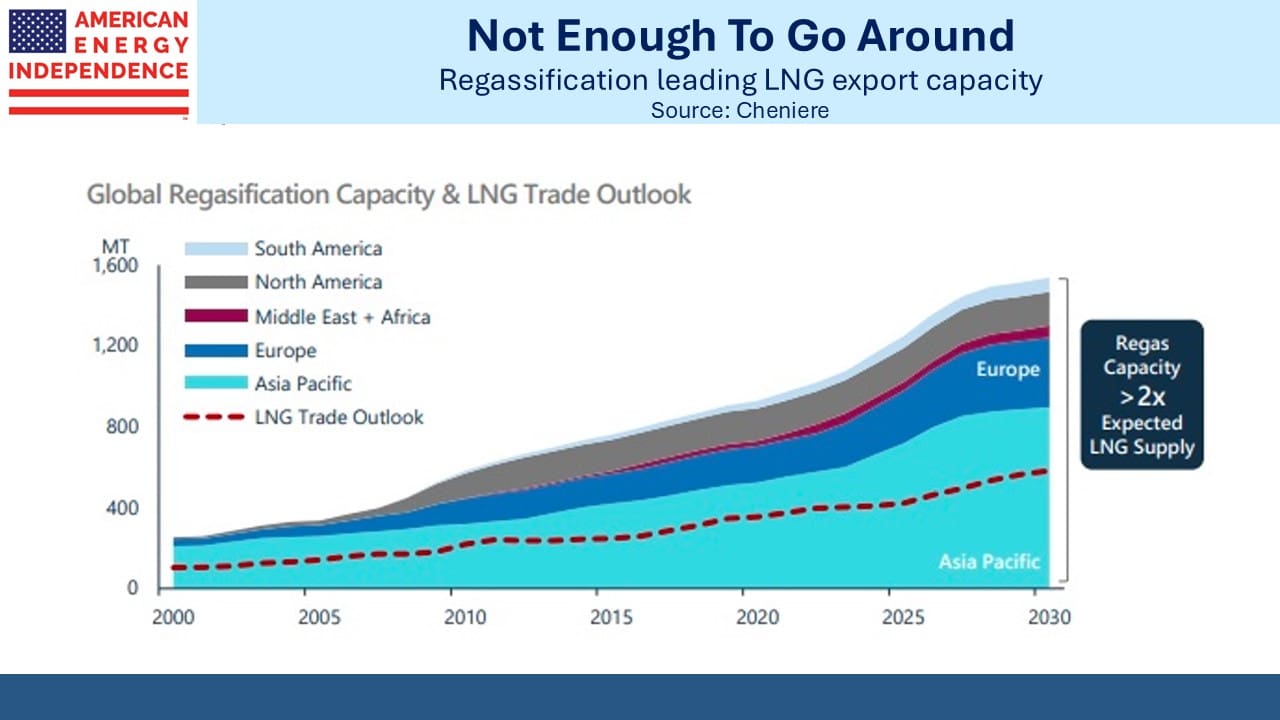
Most observers have concluded that ten-year energy forecasts are uncertain and therefore not much different. Just the Cloudburst and Stargate deals could consume 1% of US gas output and suggest that natural demand forecasts could be revised higher.
The climate extremists’ view of the energy transition is undergoing a reassessment. The Army Corp of Engineers has temporarily paused 168 permits for renewables projects. Total CEO Patrick Pouyanne stopped investment in offshore US wind following the election, although allowed that it could resume after four years.
Shell recently wrote off their investment in the Atlantic Shores wind project that was planned off the coast of New Jersey. Even though New Jersey is unfortunately a very blue state, offshore wind turbines are wildly unpopular with Republican residents of the Jersey shore. Their complaints include the spoiled view and the construction required for high voltage cables to bring the power through beachfront communities.
Atlantic Shores now looks unlikely to progress, cheering the red part of the garden state where we have a summer home. Newark Airport’s Terminal A still sports ads promoting the project. I expect they’ll soon be removed.
We don’t make a living forecasting EV sales, but if pressed would suggest they’re going to be soft. The rollout of charging stations funded under the Inflation Reduction Act has been slow, with only 176,000 in place by October, just 22% more than a year earlier.
The White House wants to stop building new charging stations. Withholding funding may ultimately be over-ruled by the courts, but the uncertainty about charging availability is likely to dissuade many potential EV buyers since range anxiety is one of their biggest concerns.
Volkswagen is slashing capacity at its EV factory in Zwichau, Germany only five years after it was hailed by former Chancellor Angela Merkel for being an EV-only facility. Meanwhile BMW plans to continue investing in internal combustion engines, hedging its bets.
Last year Ford lost $5.1BN on EVs and expects this year to be worse. Western auto companies are switching to EVs faster than consumers, with deleterious financial results.
Many Republican voters were drawn to Trump’s promise to “drill baby, drill” during the election. Energy investors are less enthusiastic. They remember the poor returns under Trump 1.0 that were reversed under Biden, even though in 2019 he pledged to end fossil fuels.
So it was mildly surprising to see Enterprise Products Partners (EPD) cancel their plans to build the Sea Port Oil Terminal (SPOT) off the coast of Texas. This would have accommodated some of the largest crude tankers, but EPD found insufficient customer interest to proceed.
Energy infrastructure usually gets built only when firm commitments to use it are in hand. This shows that in spite of Trump’s pledge to boost oil output, financial returns need to be there. E&P companies are less enthusiastic. Financial discipline continues, which should appeal to energy investors.
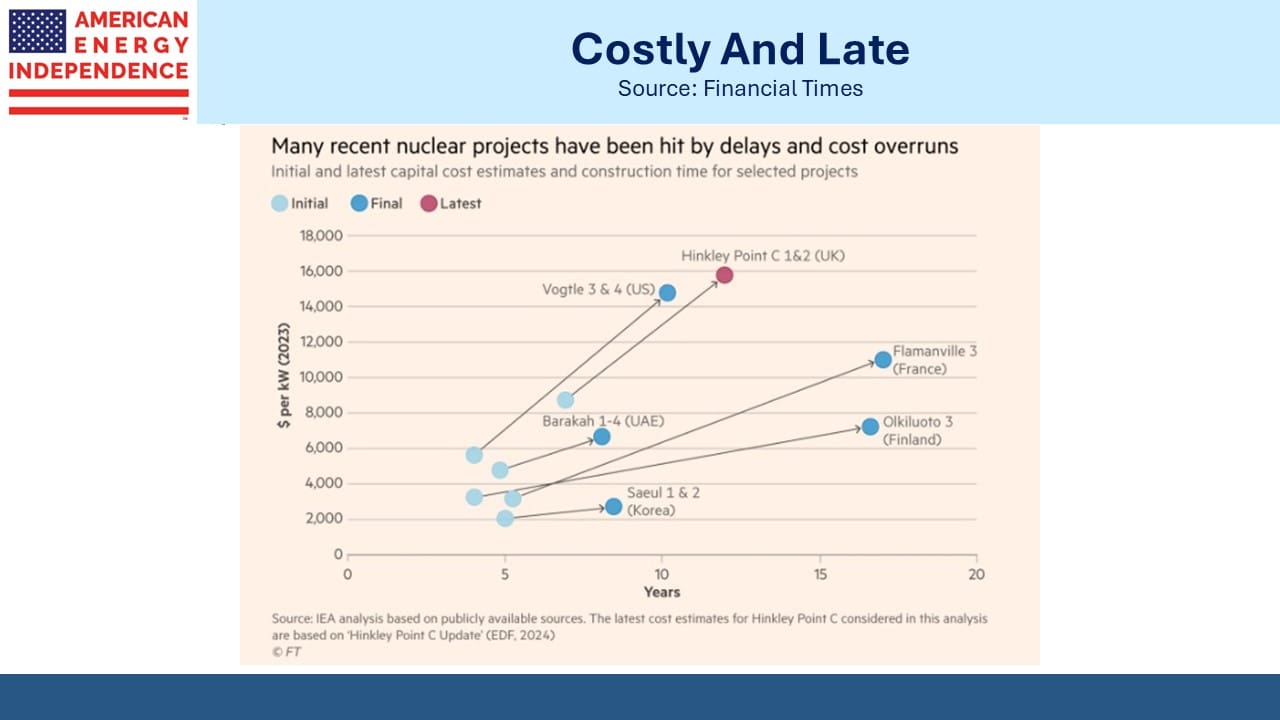
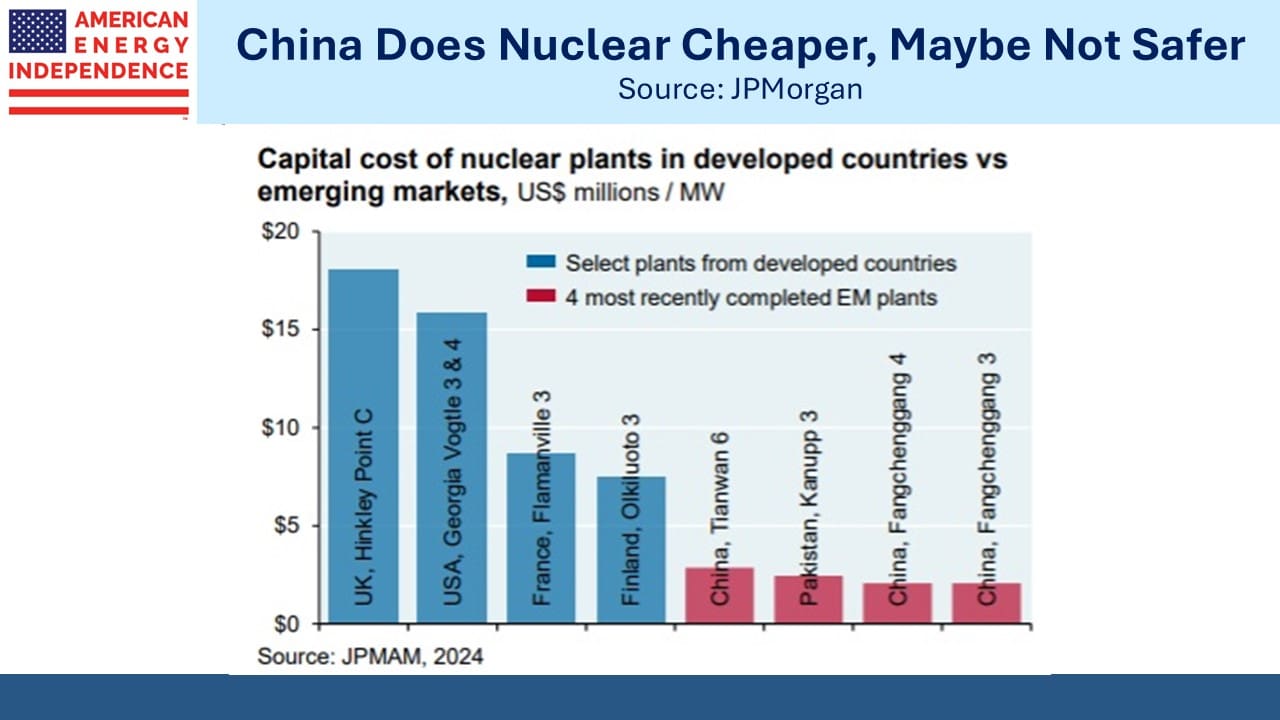
Finally, a follow-up to our recent video (watch Why Not Nuclear?). The International Energy Agency found that nuclear plants delivered since 2000 in the US and Europe were on average eight years late and cost two-and-a-half times their original budget.
The nuclear industry desperately needs to settle on standard designs that will allow economies of scale in components and simplify the regulatory process. Britain’s Sizewell C plant is designed to match as closely as possible the Hinckley Point C reactor where construction began in 2016.
US nuclear manufacturer Westinghouse was forced into bankruptcy in 2017 because of cost overruns at its Vogtle plant in Georgia, where completing units 3 and 4 took twice as long at double the projected cost.
Having learned from this experience, newly capitalized Westinghouse is negotiating to build plants in Ukraine, Poland and Bulgaria based on its AP1000 design. No modifications are allowed. Determined to control costs by sticking with what they know works, CEO Patrick Fragman says, “Basically, you can choose the color.”
The nuclear industry needs more of that.
We have two have funds that seek to profit from this environment:
Energy Mutual Fund Energy ETF