Celebrating America

May 17 represented a memorable anniversary for me as it marked 40 years since I first moved to the US. Another Brit leaving the old world for the new. I arrived on an evening flight from Toronto where I’d spent a week with family. It was my first time in NY and such was the city’s reputation I was expecting to be robbed the moment I stepped off the plane. Over those four subsequent decades my wife and I raised three children who have (so far) produced seven grandchildren (ten months to six years old). An original family of two now has two dining tables joined end-to-end to accommodate family dinner.
This is the world’s greatest country and it’s worth celebrating. July 4th is such a positive holiday. I have spent all but one of them in America since 1982. In July 1985 I was back in London for our wedding, and very appropriately my best man obtained July 4th tickets to see Bruce Springsteen at the old Wembley Stadium. Born in the USA echoed around that cavernous arena even though most (like me) were not.
I love America but I am proud to be English. England was my home until I was 19. My outlook and values were formed there. It is also a great country. On the day after Thanksgiving when England play USA at the World Cup in Qatar, I shall be waving England’s flag, the Cross of St George. You have to be true to yourself.
My children long since tired of my well-worn speech about how fortunate they are to have grown up here. I warn that the best and brightest from around the world strive to move to America, which is good for our economy but means great success requires enormous commitment. In a few years I shall offer the same homily to our grandchildren.
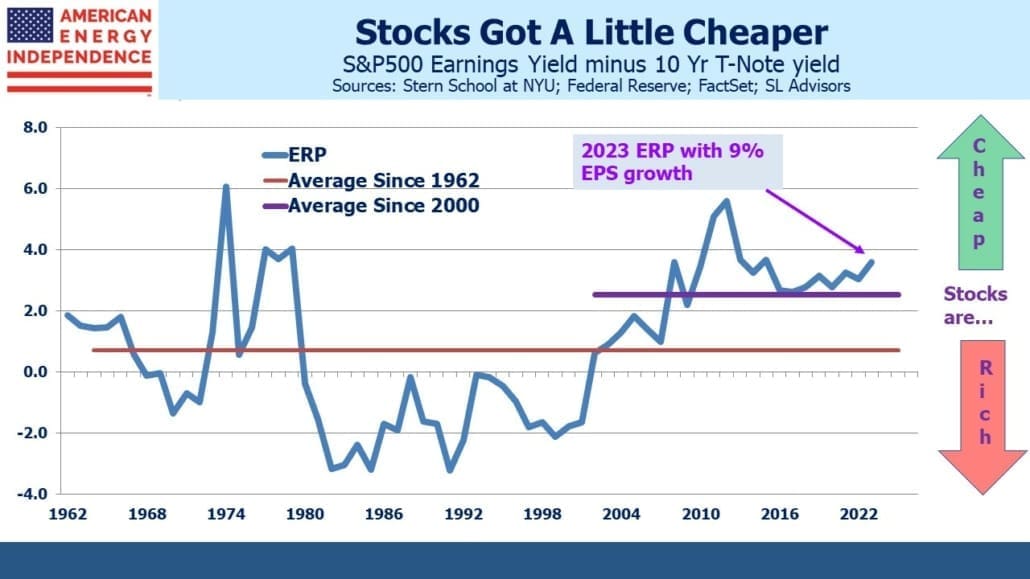
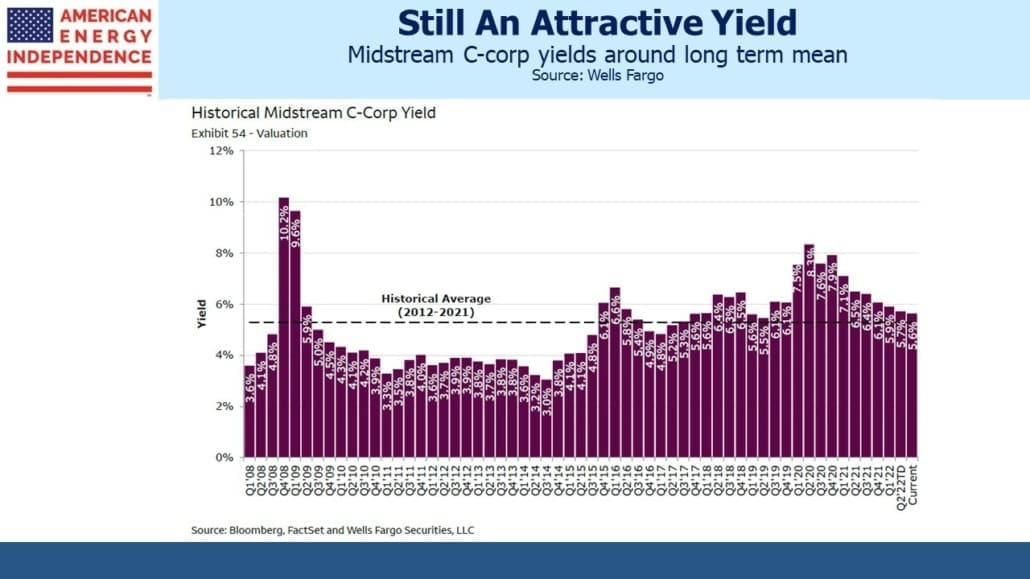
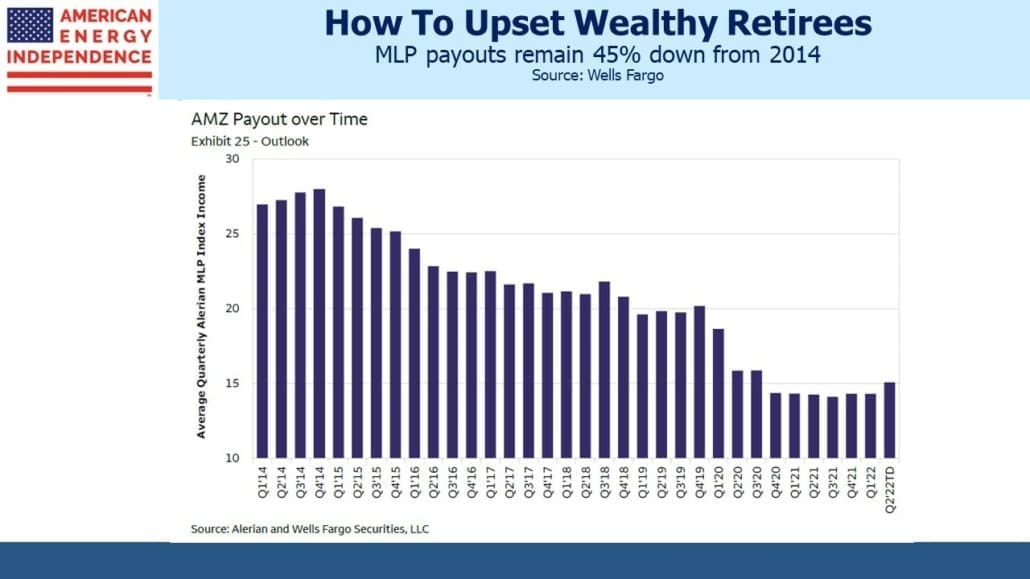
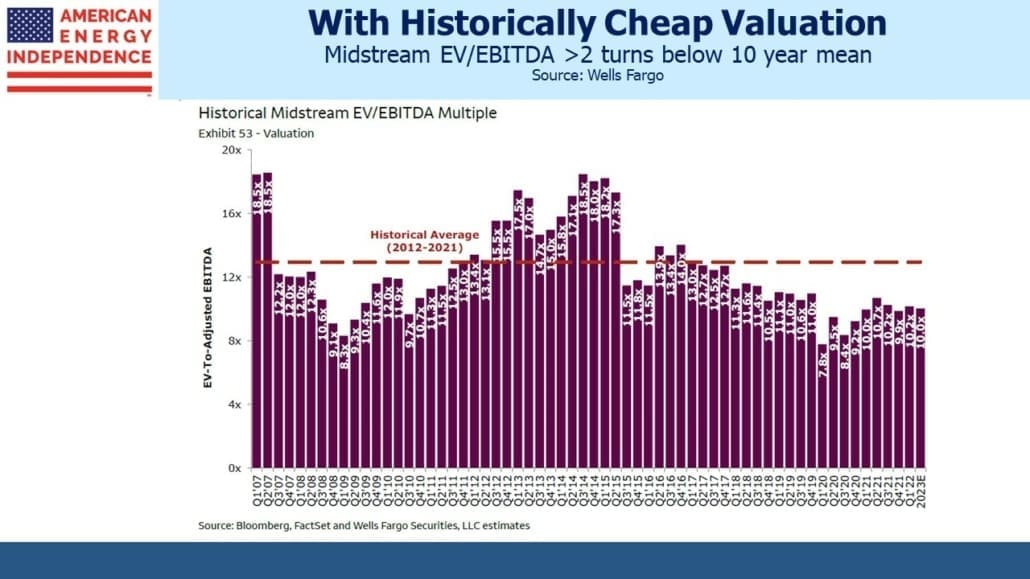
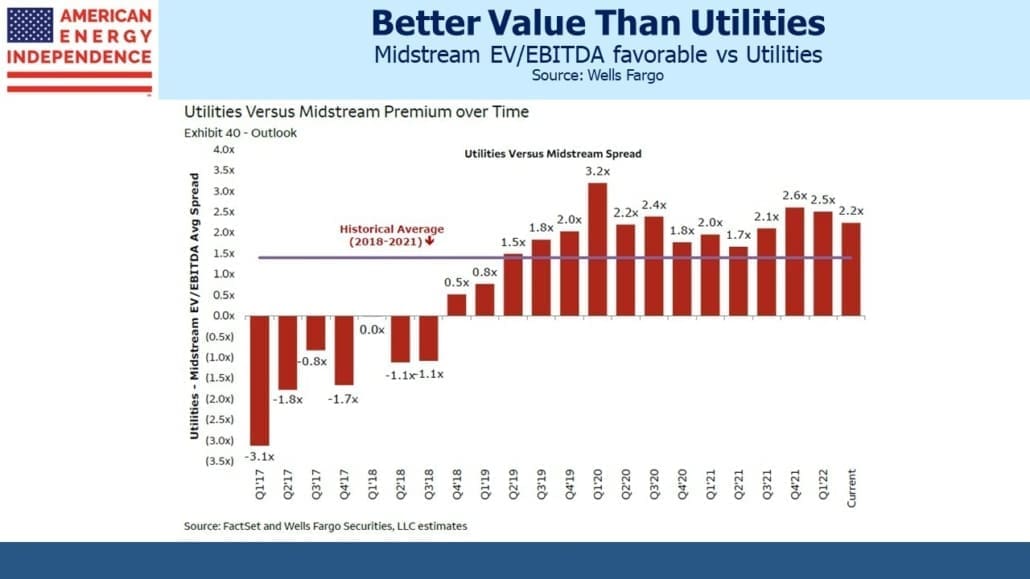
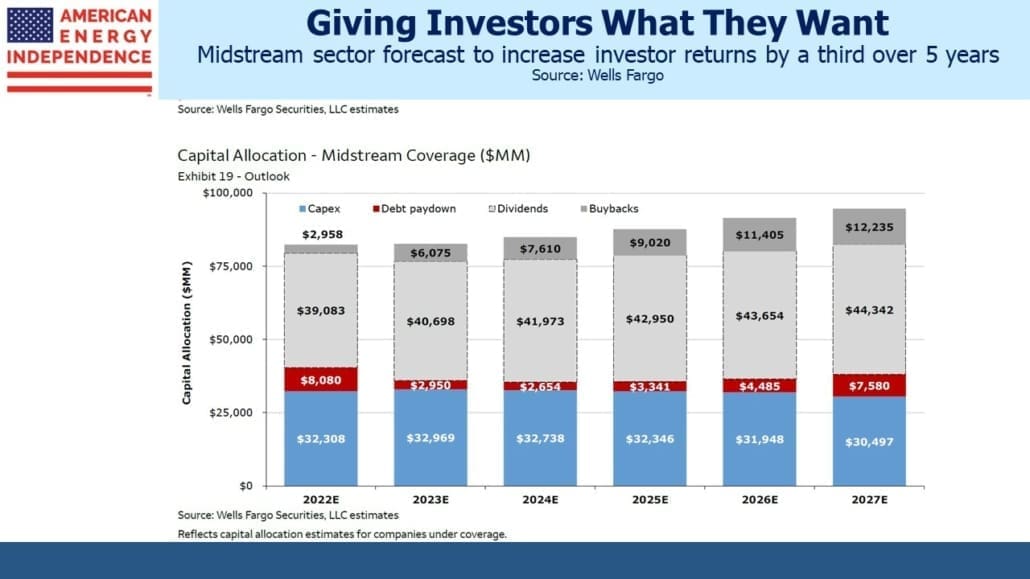
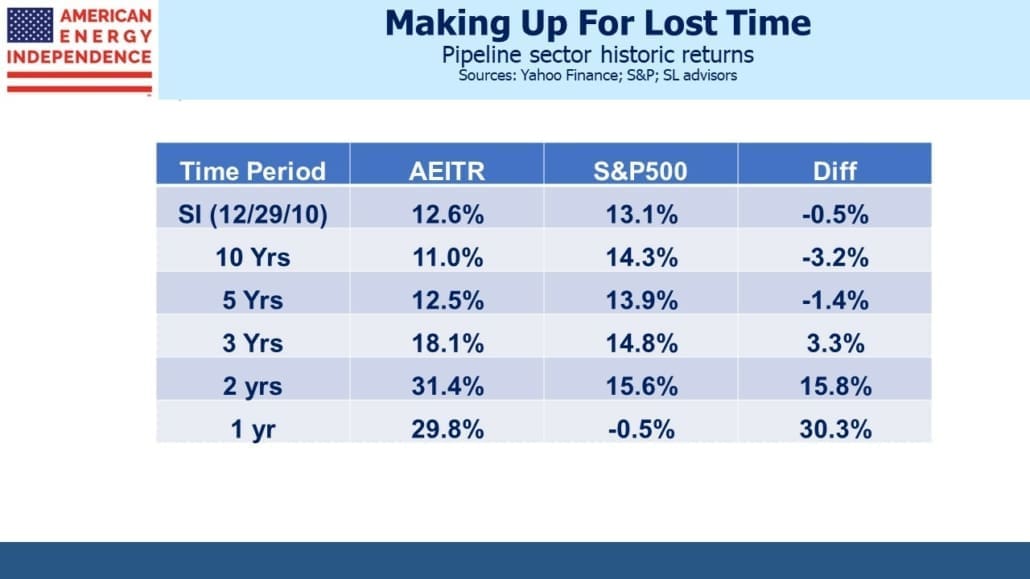
I’m told I have a sunny outlook. And why not? This year the pipeline sector is up 12%, 32% ahead of the S&P500. Some may credit my demeanor to outperformance – and while not schadenfreude, I will admit to some satisfaction in holding that rare set of investments that is beating inflation. But I felt almost as upbeat two years ago when fears of stranded assets and demand destruction ravaged energy stocks. It’s how I’m wired.
I find pessimism is more prevalent than usual. Market performance is certainly a factor, but Covid put us through the wringer. Whether you were scared of dying or frustrated at endless restrictions, we all experienced the scrambling of normal daily life. It’s left its mark. We’ve moved on, only to confront inflation and, if the Fed makes another mistake, a recession. Didn’t we just have one?
Ronald Reagan was my first president. His perpetual optimism was a beautiful sight. Today we are polarized and politics is dark. Opponents don’t just have different views, they have inferior values — if any. I have good friends who voted for Biden and good friends who voted for Trump. I generally know and don’t much care. Neither party has all the answers and both hold positions on some issues that are wrong.
One regrettable change is that today people, cities, states and even regions are characterized based on their politics. And yet for me it’s always morning again in America. Reagan’s 1984 re-election ad may look syrupy today but it still pulls my heartstrings.
If I judge America by my friends, it remains the wonderfully warm, hospitable, energetic, generous place that pulled me here in 1982. This hasn’t changed in four decades and doubtless much longer than that. Most of us meet new neighbors, business associates or golf club members regularly. Usually, my optimism about the future is confirmed.
The Fed may cause another recession, but nobody wants one. A second downturn within five years will damage America’s confidence in our government’s ability to manage the economy. We just found out how unprepared we were for a pandemic. We’re due some competent leadership. Inflation is bad but will soon seem preferable to the costs of extinguishing it. A recession isn’t yet assured.
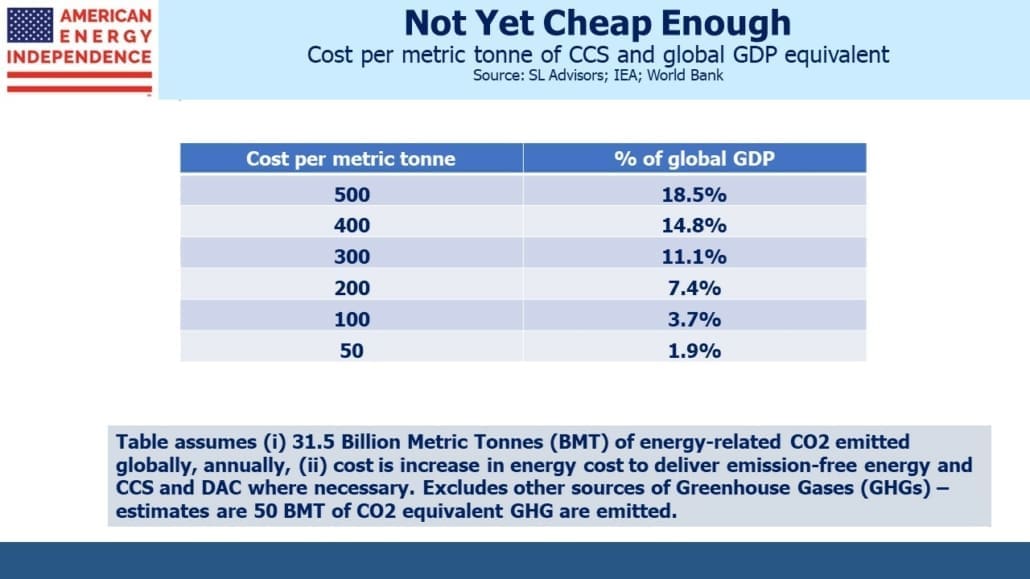
On climate change, the economic recovery from Covid and Russia’s invasion of Ukraine have quickly exposed how out of reach the zero by 50 goal is. It’s good this happened before extreme climate policy had an opportunity to decimate economic growth. Vaclav Smil’s latest book, How the World Really Works explains the physics and economics behind the energy we use (see Hydrocarbons Support The Four Pillars Of Civilization) and goes on to assert that the dramatic change envisioned by UN scientists and others is impossible.
Smil’s cold analysis reaches conclusions that climate extremists will find devastating. Accurate predictions of increased atmospheric CO2 have been around for over a century. Spectacularly wrong warnings of climate apocalypse have a similarly long history.
But Smil is no pessimist. His closing chapter predicts that, “…the most likely prospect is a mixture of progress and setback, of seemingly insurmountable difficulties and near-miraculous advances.” In other words, we’ll muddle through with reduced emissions and mitigation.
Our difficulties aren’t limited to a looming recession and global warming. But if you look around at your friends and imagine millions more like them across America, you’ll see it’s still a great country capable of meeting any challenge. I knew that when I arrived here forty years ago. I’ve been right ever since.
Happy 4th of July.
We have three funds that seek to profit from this environment:
Energy Mutual Fund Energy ETF Real Assets FundPlease see important Legal Disclosures.