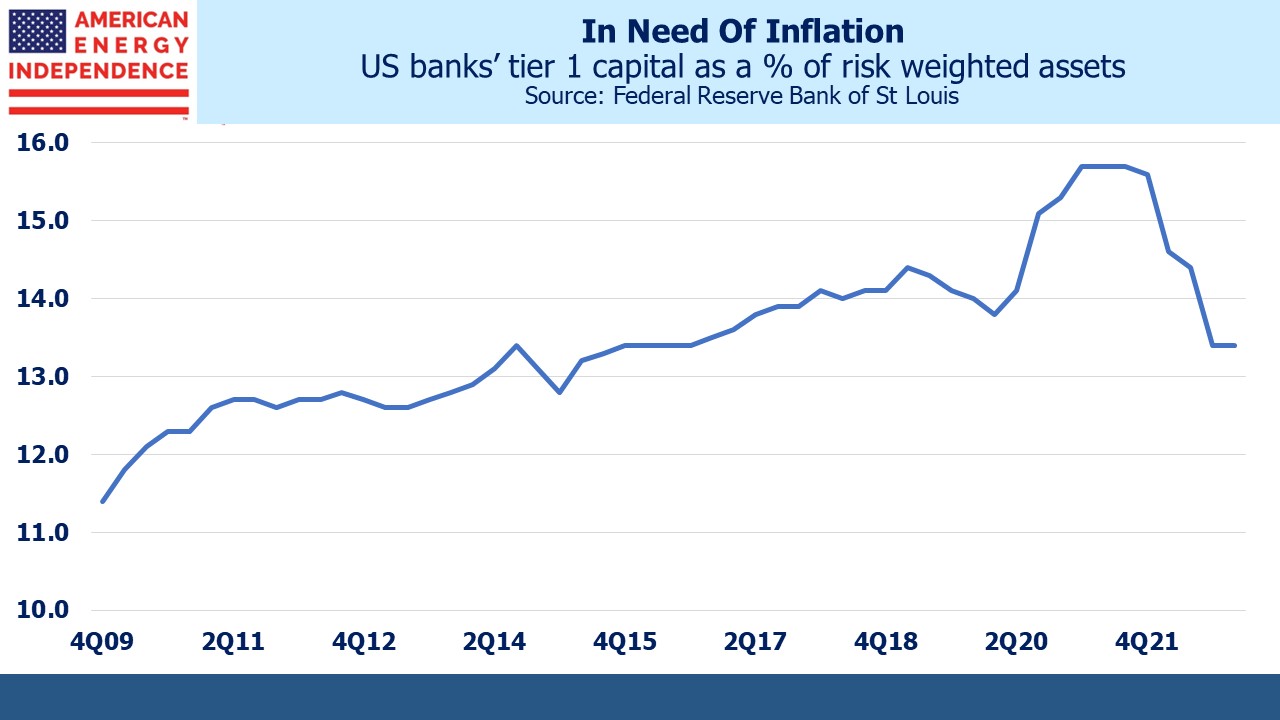
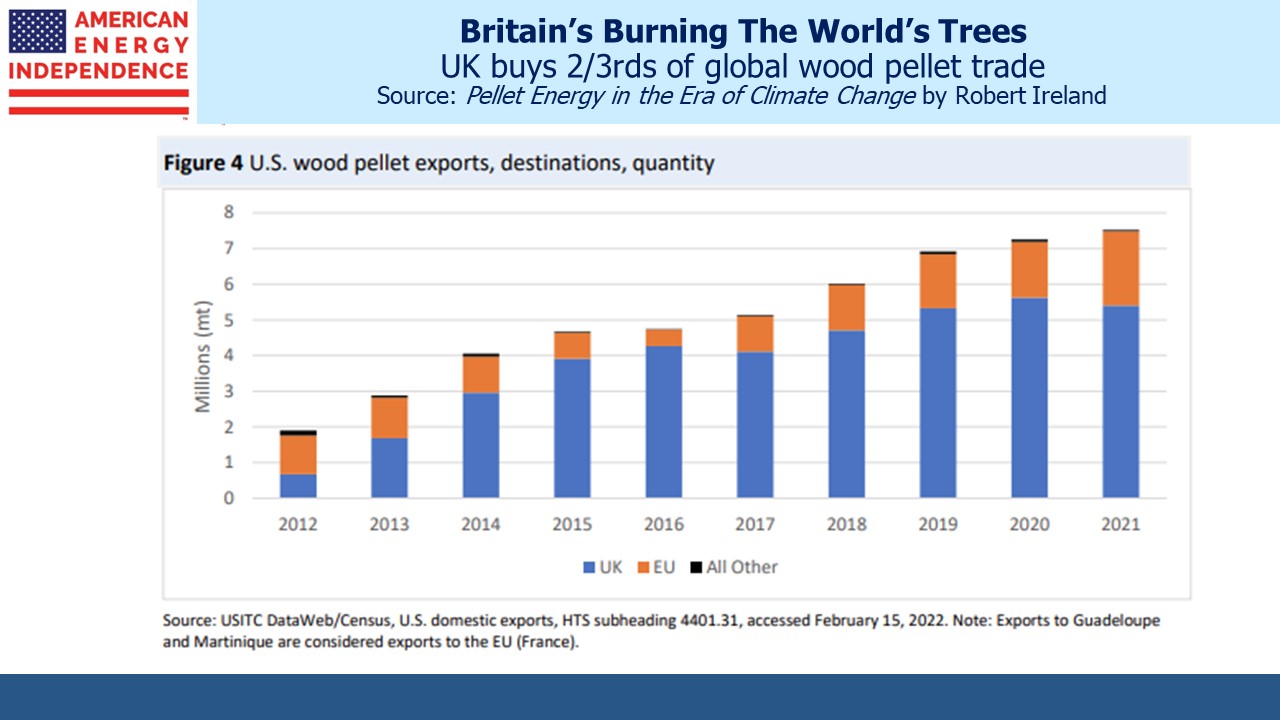
More Thoughts On Oneok and Magellan
Wall Street analysts are predisposed to be supportive of management’s M&A activities. The sycophantic posturing that precedes an earnings call question with, “Nice quarter, guys” lives in the hope of investment banking business. Hence the response of sell-side analysts to Oneok’s (OKE) proposed acquisition of Magellan Midstream (MMP) is one of mild surprise at this unlikely combination that stops short of overt criticism.
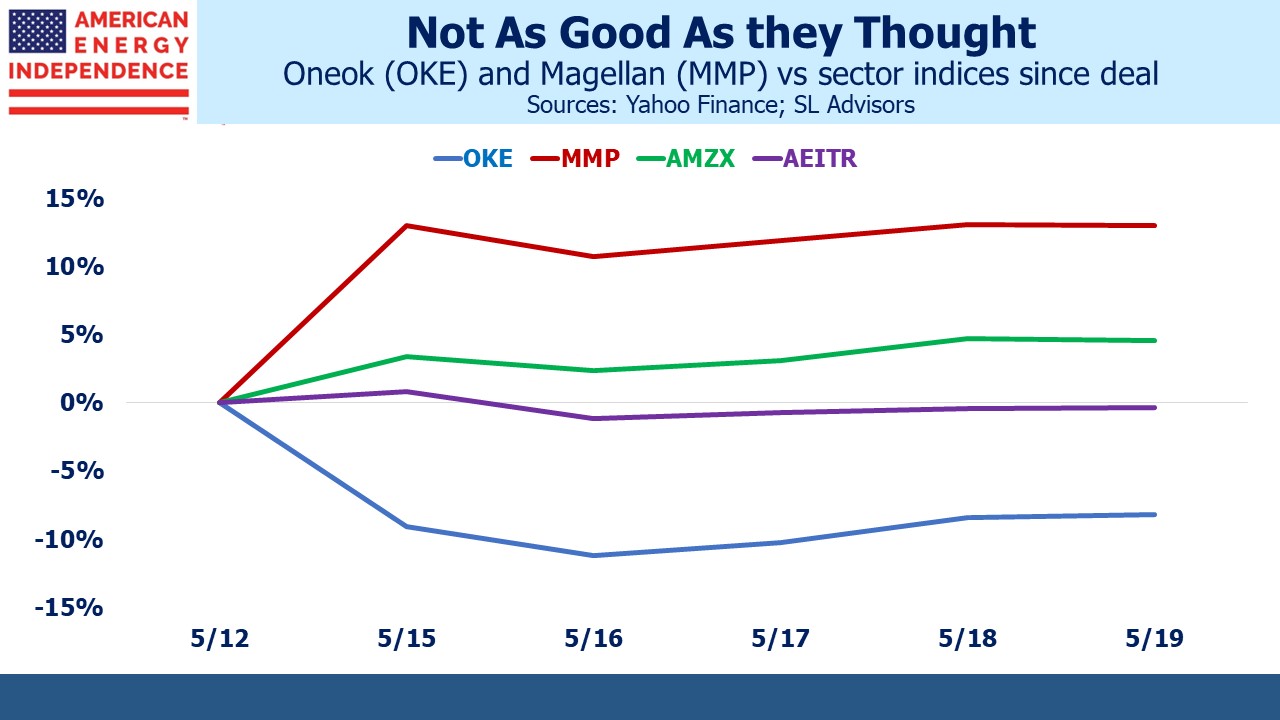
The numbers offer a less enthusiastic reception. OKE is –8% since the deal was announced, in spite of the $1.5BN tax shield and $200-400MM of annual synergies. MMP is up 13%, but this is well short of the 22% premium that heralded the deal because of OKE’s underperformance. In addition, MMP investors are facing the recapture of deferred taxes on prior distributions. This will be more for long term holders, which runs counter to the point of MLPs which is to allow long term management of tax deferrals by investors.
It’s hard to see anyone other than a recent MMP investor being untroubled by the recapture. The cohort of long term MMP holders may be too small for their votes to disrupt the deal. MMP has presumably analyzed this closely. But financial advisors who hold MMP in client accounts will not relish explaining any unexpected tax bill to clients.
An investor who owned OKE and MMP in proportion to their relative market caps is down 2.2%. By contrast, the Alerian MLP Index (AMZX) has gained 4.8% since the deal, partly due to MMP’s jump but also because traders have anticipated a rebalancing from MMP once it disappears into the shrinking group of remaining MLPs. In other words, the investors who have done best out of this deal are the ones not involved in it.
If the transaction ultimately closes, enthusiasm will be muted. The proposed OKE acquisition of MMP is a solution to a problem nobody has.
Turning to the regional bank crisis — a few weeks ago I shared my experience as treasurer of our Naples co-op in trying to earn a fair interest rate on our cash (see Some Banks Are Having To Pay More). We recently switched banks and left the 3% deposit rate that we had only achieved through persistent complaints. Banks operate on the assumption that you don’t know where treasury bills or Fed Funds are.
Our new bank relationship began at 0.25%. The initial response when I requested a competitive rate was that I should point out a competitor’s rate and they would then consider the matter. I responded that 0.25% was so off-market that it was unworthy of such effort and that they were insulting my intelligence. Days passed with no response, and finally they improved to 2%. This is from a bank whose market cap has shed two thirds in the past eighteen months.
So we’re going to open a brokerage account and buy treasury bills which yield 5%. It creates some additional administrative work, but such offensive behavior demands it. This is how one regional bank will lose a $500K deposit. Banks behave as if we’re stupid, or lazy. Their prior experience may justify such a stance, but it hardly seems like a stable business model to hold your customers in such low regard.
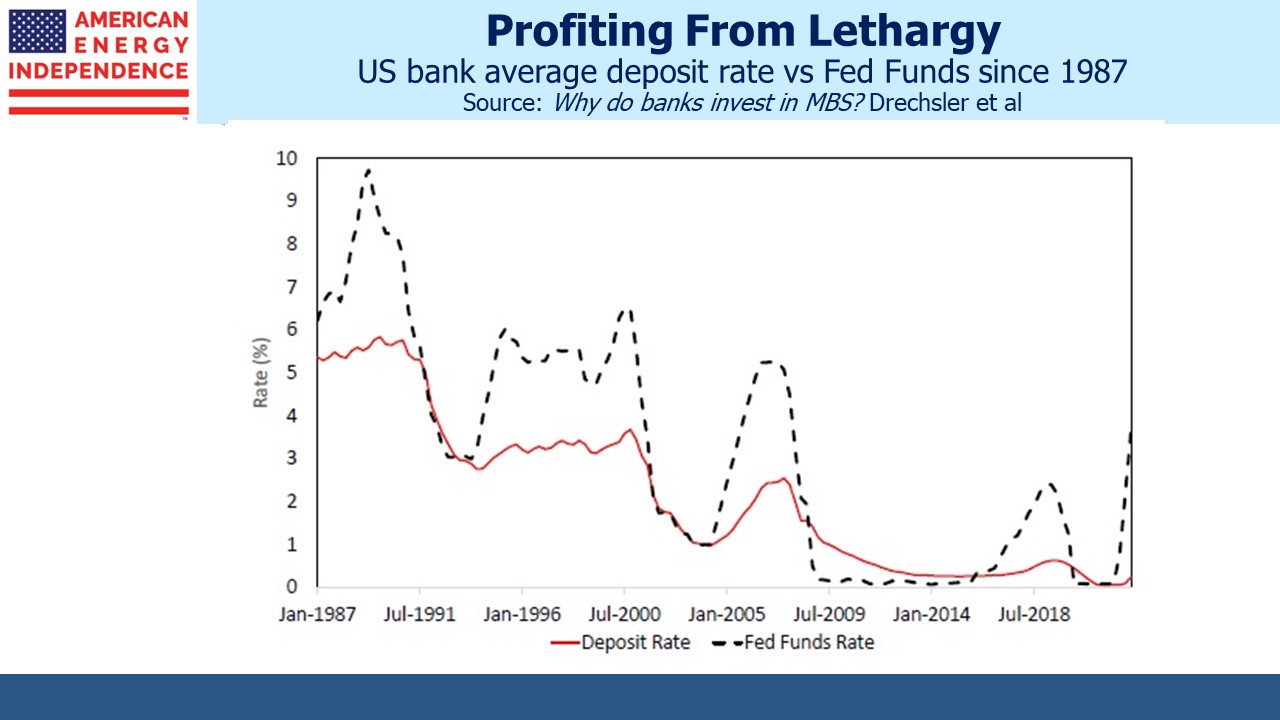
The question regional bank investors must answer is whether large numbers of depositors will react like us. Banking services need to be paid for. Banks rely on paying a discounted rate on deposits. The last time Fed funds traded above 2.5% was in 2008 before the Great Financial Crisis (GFC). Since then, deposit rates near zero haven’t represented much of an opportunity cost for customers.
Now they do, and in the intervening fifteen years moving money and gaining access to information have only become easier. Banks don’t seem willing to create linked brokerage accounts that can own treasury bills, and information about deposit rates for business clients is kept intentionally opaque. They don’t make it easy.
Nonetheless, foregoing a couple of per cent on $250K might strike many depositors as a steep price to pay for banking services.
If competitive pressure forces deposit rates higher, net interest margins will be squeezed. The argument against marking to market bank holdings of securities rests on the notion that deposits are sticky and when rates are rising the value of that stickiness (ie the discount to treasury bill yields) increases. But this is based on past behavior. How depositors reacted to rising rates prior to the GFC may not be a useful guide today. Deposits can leave, at times quickly. Regional bank investors will find out in the months ahead how responsive savers are to more competitive rates from the US Treasury.
We have three funds that seek to profit from this environment: