Will Energy Price Caps Work?
Few should be surprised that Russia has shut off all natural gas to western Europe, on a timing of their choosing not Germany’s. EU countries and the UK are implementing price controls and residential subsidies in various forms to cushion the blow from electricity prices that have risen as much as 10X over the past year. Italy plans to limit apartment thermostats to 66°F this winter.
Newly minted UK PM Liz Truss is considering a £100BN aid package that might reach £135BN ($155BN), around 5% of GDP. European governments are covering most of the increased cost of energy for households and/or waiving taxes, via loans to providers. The shortfall will be made up through future tax revenue and gradually increasing prices.
For many there is no plausible politically feasible alternative. By subsidizing demand, such policies delay the demand destruction that’s necessary to bring European energy markets into balance. It’s difficult to see governments exiting the subsidy business anytime soon. Since natural gas is often the marginal source of power in most European markets, it sets the price of electricity.
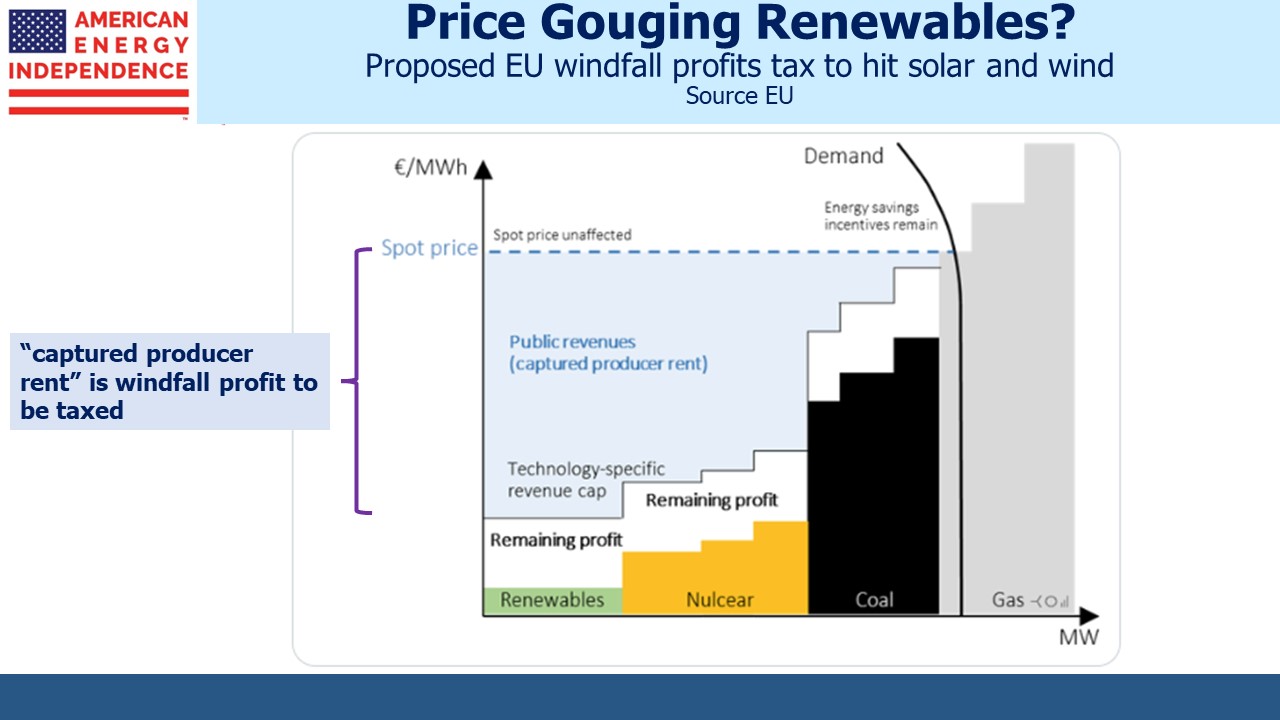
This has perversely created windfall profits for renewables businesses, which now face the prospect of a windfall tax across the EU. Ironically, solar and wind power generators are the big winners because their costs haven’t gone up. This ought to create strong incentives to invest in additional renewables capacity, except that’s where the proposed windfall profits tax will fall most heavily. European energy policies are turning into perhaps the biggest public policy failure since World War II. It should be called the Merkel Energy Crisis since Germany’s recently retired chancellor was such a significant architect.
At least Klaus-Dieter Maubach, the CEO of Uniper, Germany’s biggest importer of natural gas, had the honesty to concede that trusting Gazprom to be a reliable supplier and the absence of LNG import infrastructure were both mistakes. In a recent video he noted that wholesale power prices were as much as 20X the level of two years ago. Maubach warned that worse was to come for European customers.
Price caps on Russian crude oil are likely coming, although we think their enforceability will be difficult. Western insurance companies provide coverage on around 90% of seaborne trade, and the G7 plan relies on the threat of withholding such insurance from buyers of Russian crude oil that refuse to comply with whatever price cap G7 imposes.
This seems simplistic. If India wants to buy Russian crude, insurance could be provided by either country. It’s also possible such a move will induce OPEC+ to regard it as interfering with their price setting ability and trim demand. Yesterday they announced a modest reduction of 100K barrels per day.
The bottom line is that western sanctions on Russian energy supplies have so far served to raise prices and enrich Russia.
Markets continue to regard developments as positive for the US energy sector. Long term demand for US LNG seems assured. The enormous price difference between the US Henry Hub natural gas benchmark and both the TTF European and JKM Asian ones is likely to prevail for several years given the time it takes to add LNG export capacity.
This should continue to underpin US companies involved in natural gas infrastructure, such as Cheniere, Williams Companies and Energy Transfer. We also still like NextDecade, which is an early-stage LNG exporter we believe will soon start construction on their Rio Grande, TX facility. LNG exports are still some way off for NextDecade so it’s a more speculative holding than most midstream infrastructure companies. But we think the stock has substantial upside from current levels assuming ultimate success.
The US isn’t totally immune from poor energy policies. California is once again asking residents to curb power consumption during a heatwave. Years of shutting natural gas power plants has increased the state’s dependence on intermittent solar, an energy source poorly aligned with peak residential demand around dinner time. All while China pumps out ever more CO2.
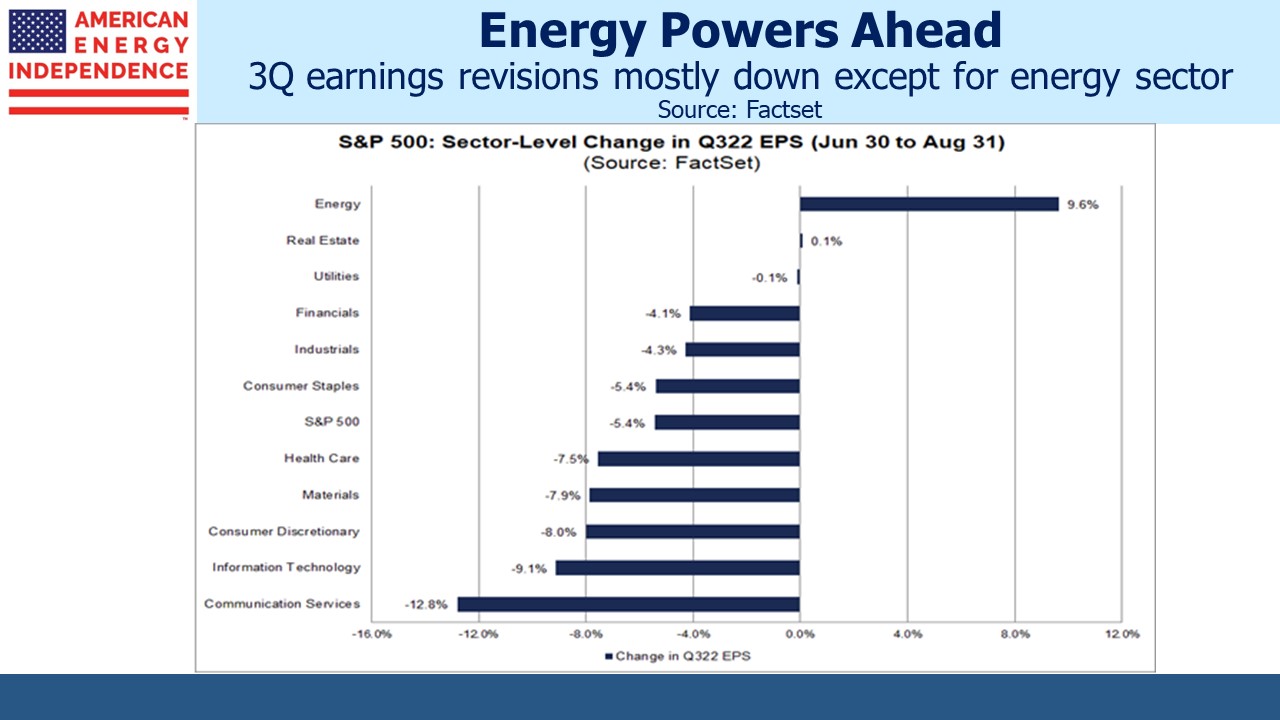
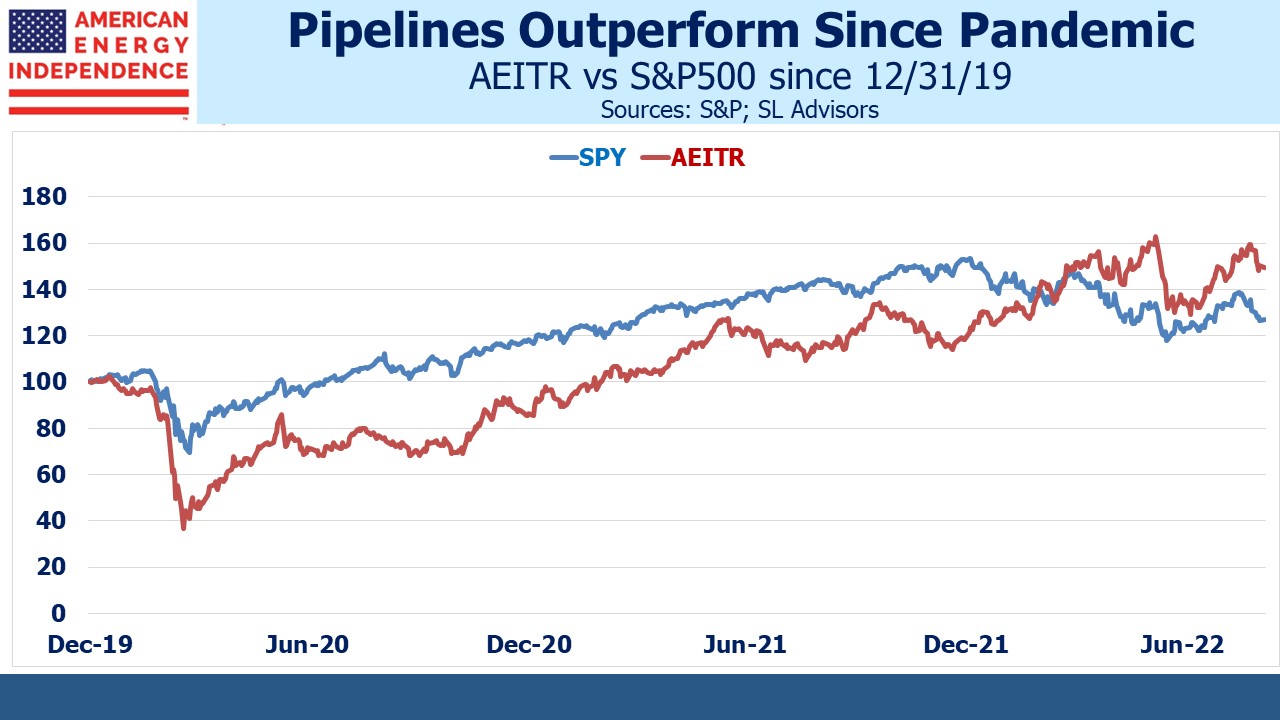
Sell side analysts have been revising down their 3Q earnings forecasts for most sectors over the past couple of months. Energy is the standout exception where the outlook continues to improve. Since the end of 2019 (ie before the pandemic) the American Energy Independence Index (AEITR) has returned 16% pa – solidly ahead of the S&P500 at 9% but still not euphoric.
The components of the AEITR have a market-cap weighted free cash flow yield of 10% and leverage (Debt:EBITDA) of 3.7X. The sector continues to generate growing cashflows with strong balance sheets.
We have three funds that seek to profit from this environment:
Please see important Legal Disclosures.