MLP Investors Digest Supply
My partner Henry Hoffman and I spent Thursday last week at the Capital Link MLP Investing Forum in New York. The mood was cautiously optimistic but certainly wary of another commodity-linked swoon in prices. Meeting one-on-one with company managements is often the best part of such events. We had a very useful discussion with Crestwood’s (CEQP) Heath Deneke, COO and President of their Pipeline Services Group, along with Josh Wannarka, Investor Relations. We gained an improved understanding of CEQP’s strategic partnerships with long-time sponsor First Reserve and JV partner Con Edison. Both these relationships are important to CEQP’s growth prospects and represent a key differentiating feature.
Companies have been reporting 4Q16 earnings over the past few weeks. For Master Limited Partnerships (MLPs), the generally positive outlook has been at odds with market performance. In February the “Trump Bump” rally in the S&P500 was only weakly reflected in MLPs, resulting in +4.0% versus +0.4% respective performance.
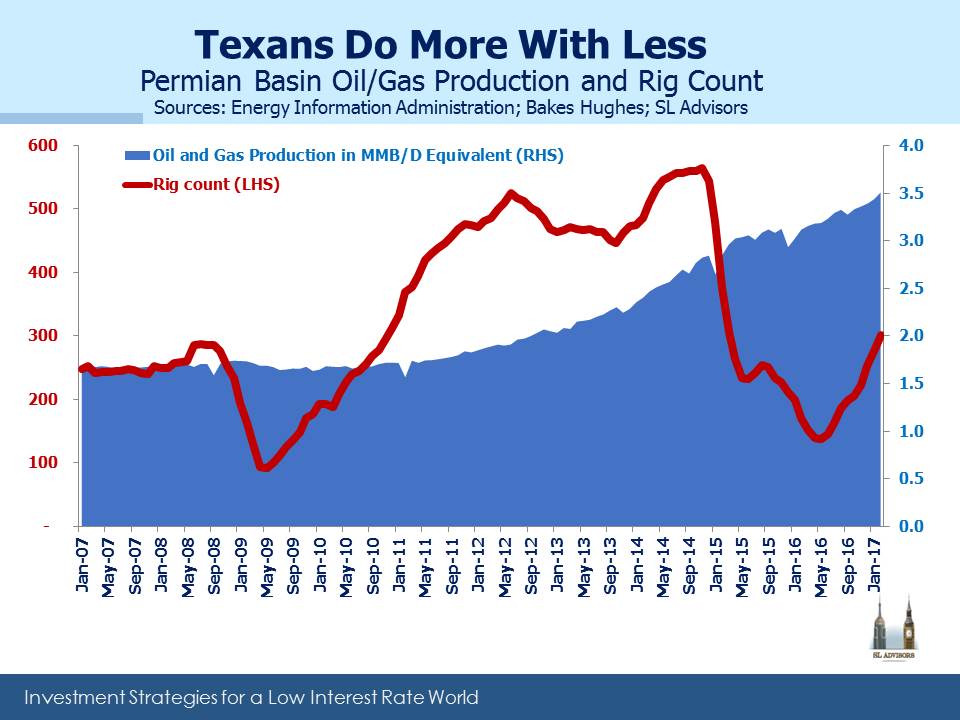
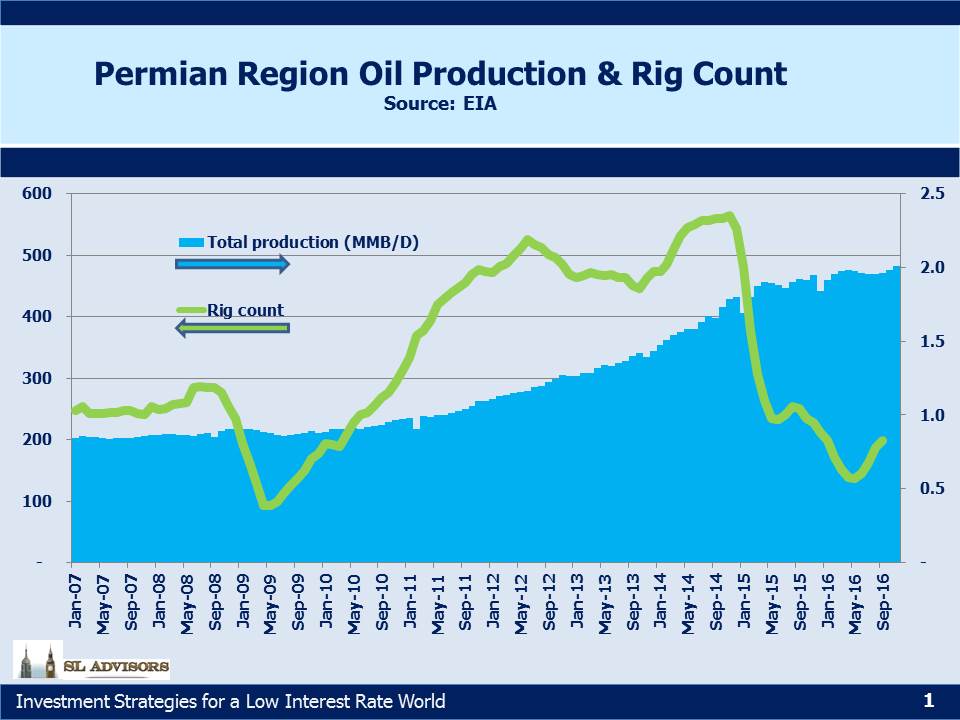
The Permian Basin in West Texas remains the hottest area for shale production in the U.S. Earnings calls with those companies active there focused on growing production and whether the existing take-away infrastructure would be sufficient. The U.S. produces around 9 MMB/D (Millions of Barrel per Day) of crude oil. Approximately half of that is “tight”, and half of that comes from the Permian Basin (currently producing around 2.25MMB/D). When combined with Permian natural gas output on an energy equivalent basis, production is almost 3.5MMB/D.
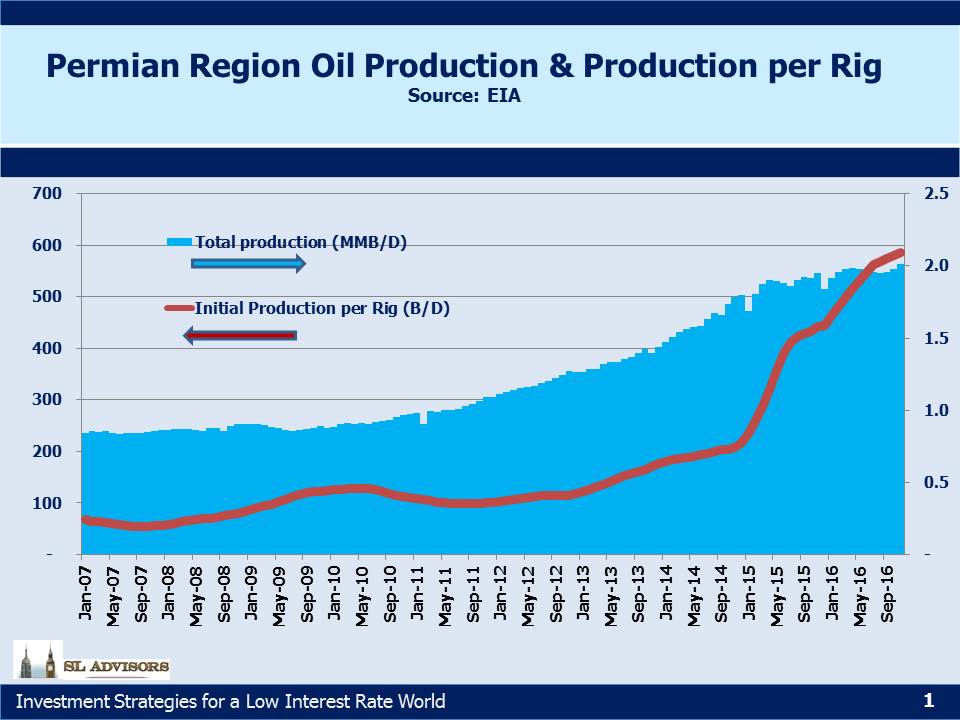
Permian output was the most resilient of any of the major shale plays through 2015-16 with production continuing to grow almost oblivious to the collapse in pricing. This was entirely due to the ongoing productivity improvements that have led to high single digit annual cost improvements for Exploration and Production companies operating there. The Energy Information Administration (EIA) forecasts U.S. crude production will increase by another 0.5MMB/D 2017-18, and much of that is likely to occur in the Permian.
Reflecting the increased production forecast by E&P companies, several MLPs with Permian assets announced plans to increase take-away pipeline capacity where needed. These include 60MB/D (Thousand Barrels per Day) on Plain’s All American (PAGP) Cactus pipeline to Gardendale, Texas, 100 MB/D on the BridgeTex line into Houston (jointly owned by Magellan Midstream (MMP) and Plains All American (PAGP)) and 300 MB/D on the Permian Express II to Nederland, TX owned by Sunoco Logistics (SXL). In addition, Energy Transfer Partners (ETP) has an existing 100MB/D pipeline that is currently idle but could be restarted if demand was there. In summary, industry debate on this issue revolves around the ability to move increasing volumes.
This increased production is not necessarily consistent with OPEC’s objectives when they announced their own production cuts late last year. A gently rising oil price with minimal variability is their preferred scenario. Reports indicate that some OPEC members would like to see $60 oil so as to stimulate additional long term investment in new supply, thereby lowering the odds of a short-term, ruinous price spike that could hurt demand. As we’ve noted before (see The Changing Face of Oil Supply), conventional projects with their large up-front capital commitments and long payback times are vulnerable to U.S. shale production in a way that wasn’t previously contemplated.
Relying on the spot price of oil in assessing a 10+ year project is nowadays recklessly simplistic, making investments in conventional new supply riskier than in the past. Although U.S. production is growing, it won’t be sufficient to meet new global demand plus make up for depletion from existing fields (estimated at 6MMB/D, see Listen to What the Oil Price is Saying). Gently higher prices remain the most likely outcome but there’s more risk of a sharp move up rather than down.
Exxon Mobil (XOM) CEO Darren Woods reflected this new mindset in recent comments: “More than one third of the capex [capital and exploration spending] will be invested in advancing our large inventory of … short-cycle opportunities. They are primarily Permian and Bakken unconventional plays and short-cycle conventional work programs. This component of our investment plan is expected to generate positive cash flow less than three years after initial investment.”
In other words, long payback times are risky. Short payback projects are in the U.S.
The MLP investor who feels she’s missing out on the recent equity rally is rather non-plussed by this optimistic analysis. “If you’re so smart, how come I’m not richer?”
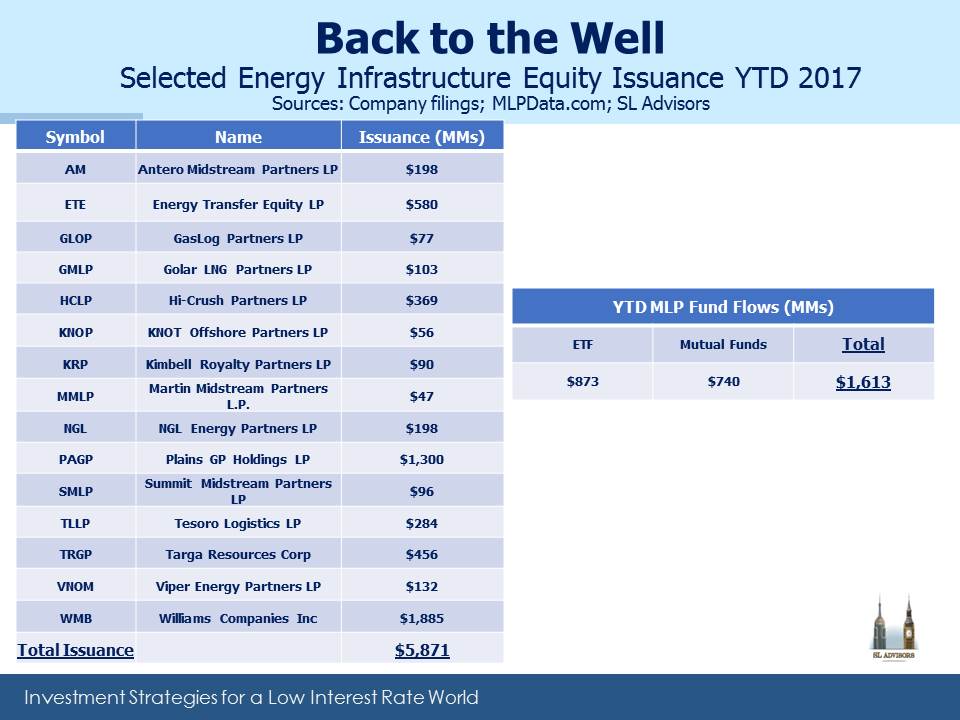
One reason is the overhang of equity being issued by some MLPs, to strengthen balance sheets and fund new projects. PAGP issued $1.3BN in equity; Targa Resources (TRGP) issued $450M to help fund it’s acquisition of Permian focused Outrigger Energy. There was also a sale of 7.2MM shares in Targa Resources (TRGP) by a private equity investor who converted warrants acquired a year ago, booking a nice profit. And a few weeks earlier Williams Companies (WMB) raised $1.9BN. The table shows the many issues of new equity in recent weeks, as well as inflows to mutual funds and ETFs. It’s an incomplete picture, and by definition the almost $6BN in equity sales has been matched with an equal amount of buying. The use of this new capital, mainly to strengthen balance sheets and fund accretive growth, is definitely positive. But over the near term this new supply approximately absorbed 1Q distributions paid by MLPs.
Another headwind is that it’s once again been a mild winter. Rapidly receding snow has plenty of appeal, but the downside is that it reduces natural gas demand. MLPs care about volumes, and we’re using less natural gas than expected to heat homes in the north.
Nonetheless, valuations remain compelling. For the momentum investor it’s easy to feel good buying stocks. But for the more discerning who care about values, at a time when most sectors of the stock market are close to all-time highs, the Alerian Index yields around 6.8%, 4.6% above the ten year treasury and still 1.2% wider than the 20 year average. We may have bounced 75% off the low of February 11th, 2016 but still remain 27% off the August 2014 high.
We are invested in CEQP, MMP, PAGP, TRGP, & WMB