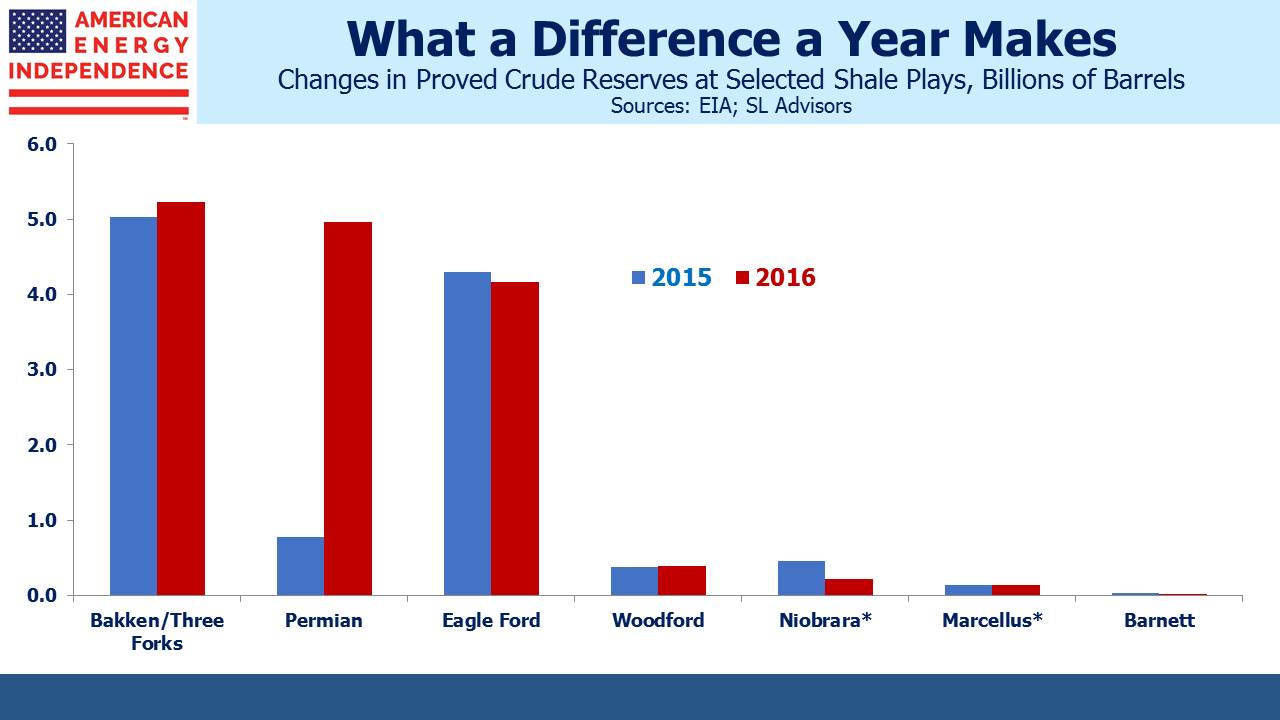
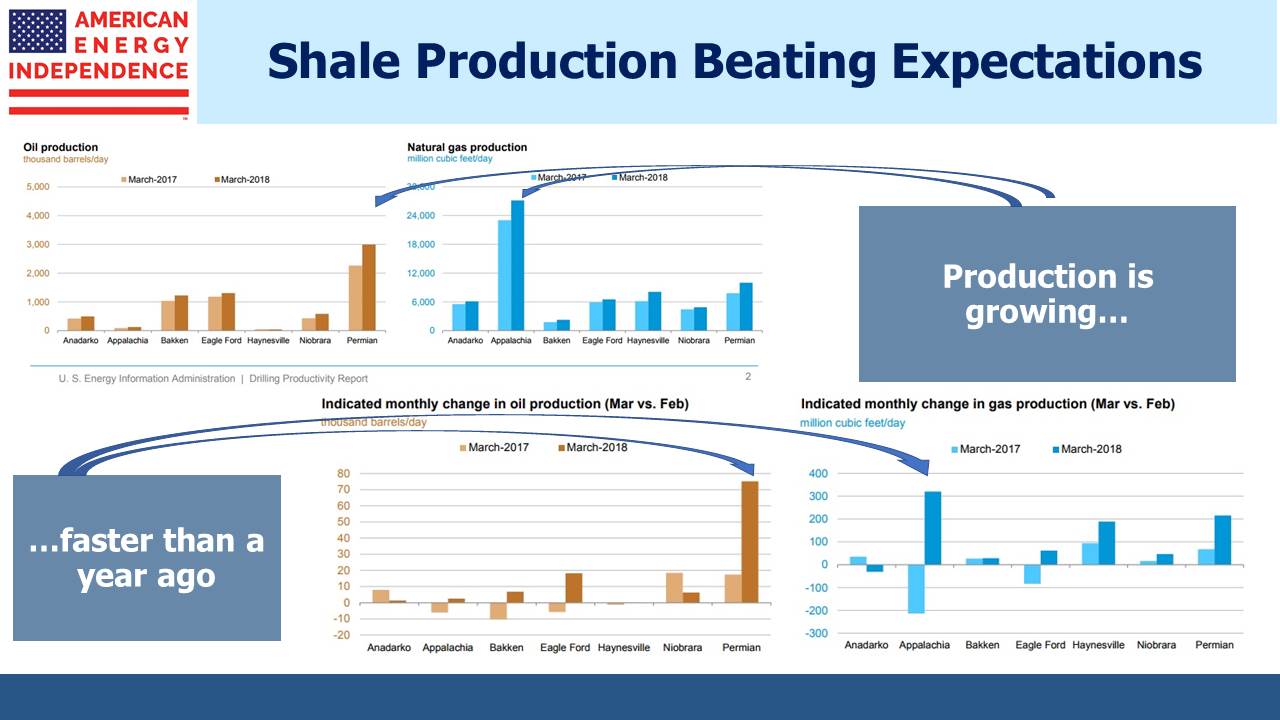
Are MLPs Going Away?
MLP investors have certainly seen their conviction tested of late. Poor stock performance was recently compounded by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s (FERC) ruling on cost of service contracts earlier this month. Although MLPs don’t pay tax, interstate natural gas pipeline tariffs based on cost-of-service have historically included an allowance for taxes paid by their investors. Following a court challenge by United Airlines, FERC has now disallowed this practice.
Since last year’s tax reform, MLPs have already included lower imputed tax expense in their guidance. After the FERC ruling, most firms reaffirmed prior guidance, since the immediate impact of the change is quite narrow. However, the loss of the tax allowance will impact gradually over the next few years. Along with the drop in the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%, it further reduces the relative advantage of MLPs compared with corporate ownership of energy infrastructure assets.
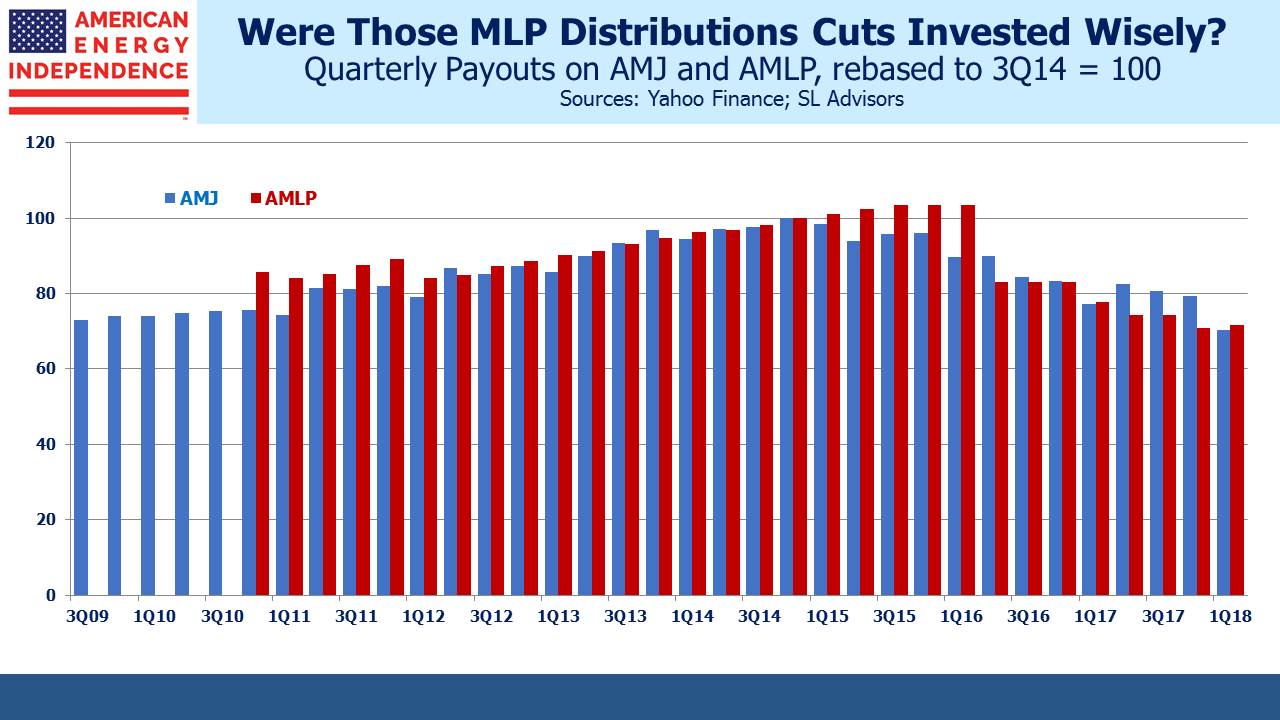
The trend favoring corporate ownership is well established. As we’ve written before, MLP investors (generally, older wealthy Americans) want their distributions and don’t much care for the distribution cuts that have been necessary to finance growth projects (see Will MLP Distribution Cuts Pay Off?). These investors are income-seeking, not total return oriented. It’s why MLP yields remain stubbornly high, and is behind the many “simplification” transactions that move assets to corporate ownership and cut payouts.
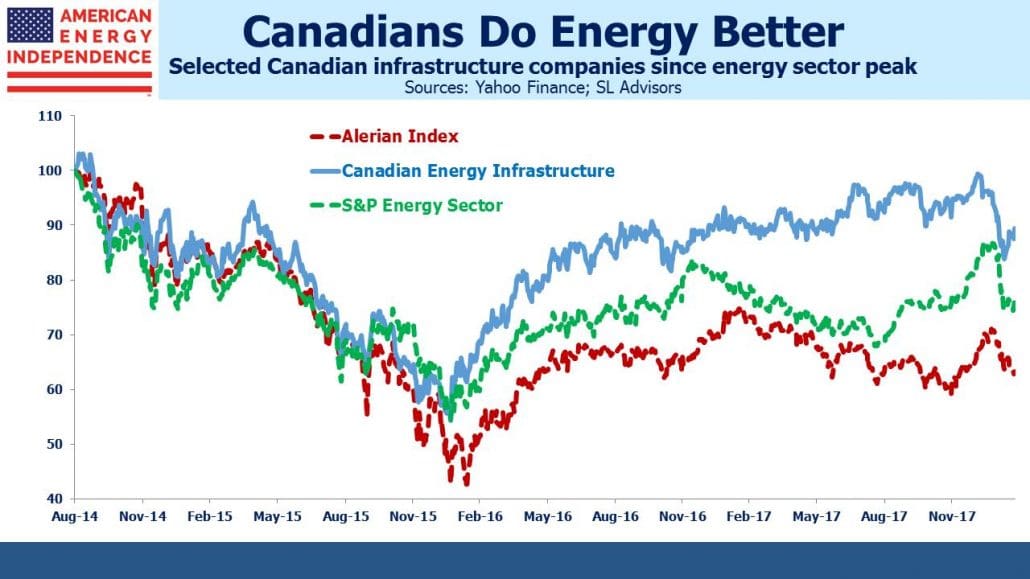
FERC’s ruling probably helps that ongoing trend towards corporations (see FERC Ruling Pushes Pipelines Out of MLPs). MLPs are complex, with a limited investor base, and are losing some of their comparative advantage over corporations because of changes to the tax code. They already represent less than half of energy infrastructure. The tax ruling by FERC doesn’t affect corporate owners, since their tax expense is real, not imputed as was the case with MLPs.
If you’re a direct holder of MLPs, as long as the assets continue to perform there’s not much reason to do anything. You may ultimately wind up owning shares in a corporation if the MLP converts, and it might even be acquired. The tax consequence of waiting is likely no worse than selling your MLP today.
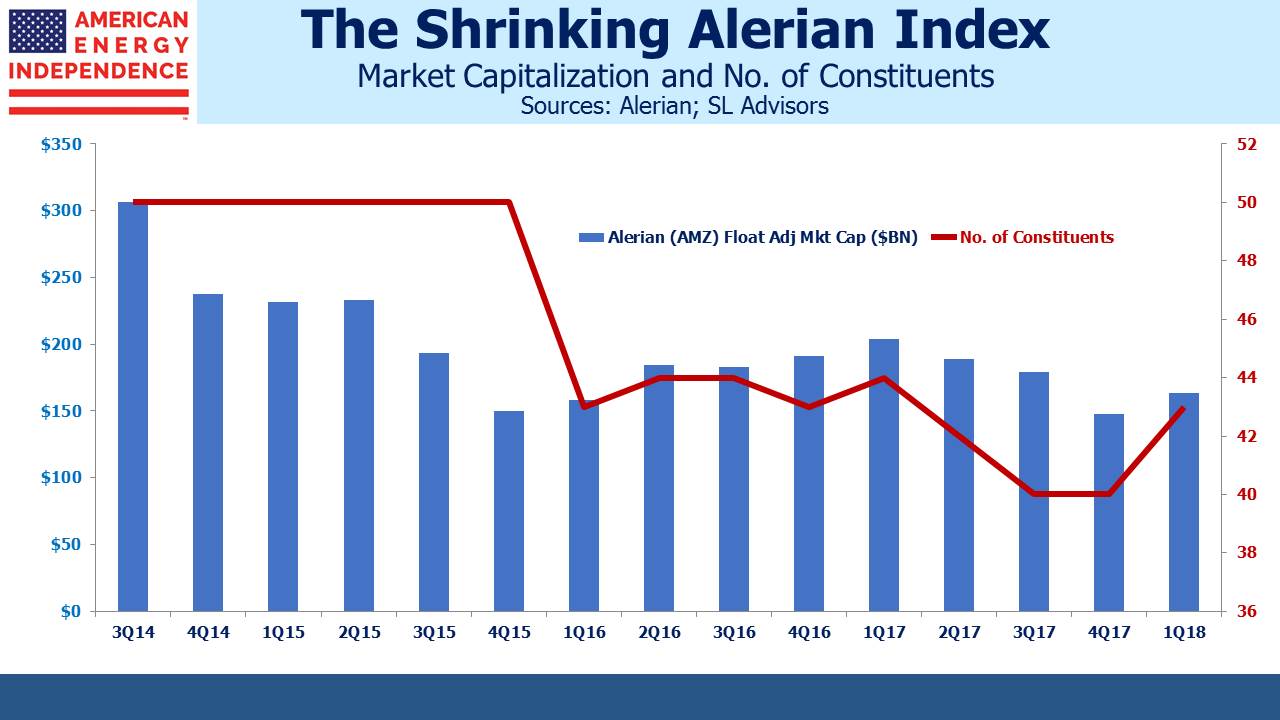
However, investors in many MLP-dedicated funds that are not RIC-compliant face a real dilemma. As the number of MLPs contracts, these funds will struggle to find enough names to own. The Alerian Index has been shrinking for some time, both in market cap and constituents. Investors in the wrong kind of fund face a corporate tax haircut as well as a declining opportunity set.
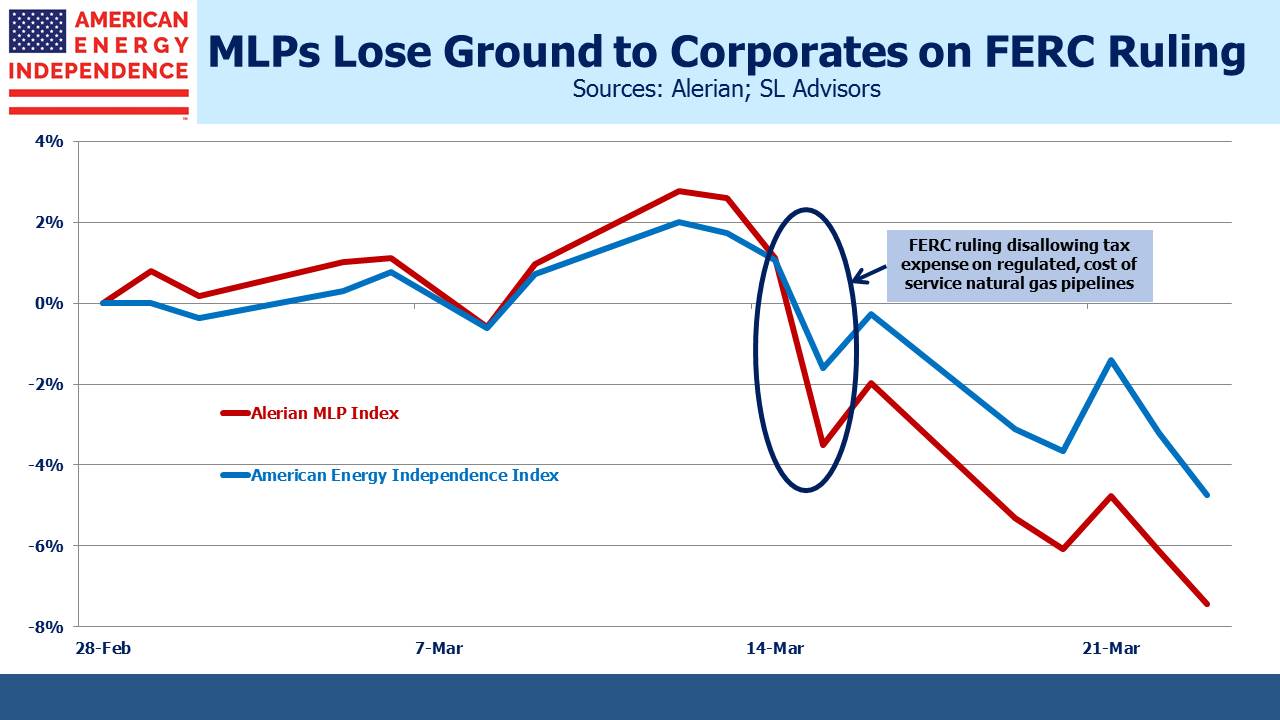
There’s some recent evidence since the FERC ruling that investors are starting to favor corporate infrastructure names over MLPs. So far in March, the American Energy Independence Index, which consists of broad energy infrastructure exposure with only 20% in MLPs, has handily outperformed the more narrow, MLP-dedicated Alerian Index by 2.7%. This outperformance has come since the FERC ruling. Anecdotally, we know some investors are switching from tax-paying funds into pass-through, RIC-compliant ones because that’s all we offer and we are seeing the inflows.
Since last Summer, we calculate that tax-impaired funds have seen net outflows, as investors have become more aware of the performance drag (see AMLP’s Tax Bondage) and the shrinking opportunity set. Meanwhile, properly structured RIC-compliant funds with no tax drag picked up almost $900MM over this time. It’s reflected in the shrinking float-adjusted market capitalization of the constituents of the Alerian Index, which is less than half of its 2014 peak, significantly lower than performance alone would imply.
The number of Alerian constituents has also shrunk noticeably since 2014. Just six names make up half its market cap, and seven have a market cap of below $1BN. Williams Companies (WMB) could well conclude that the FERC ruling means they’re better off owning their sprawling interstate natural gas pipeline network, Transco, at the corporate level, thereby eliminating MLP Williams Partners (WPZ). Enbridge (ENB) could easily absorb the remaining public float of Spectra Energy Partners (SEP) and Enbridge Energy Partners (EEP) to offset FERC’s impact on their cost-of-service tariffs. Plains GP Holdings (PAGP) will eventually covet the tax shield that would come from absorbing the remaining units of its MLP, Plains All American (PAA).
Combined, losing these four would reduce the market cap of the Alerian index by $24BN, about 17%. By comparison, the two new names added in 1Q18 (Hi-Crush Partners and CVR Refining) have a combined market cap of only $1.5BN. The Alerian MLP Index is not what it used to be.
The American Energy Independence Index has a float-adjusted market cap of $315BN, more than twice Alerian, reflecting its broader approach. Investors are starting to take note.
We are invested in ENB, PAGP and WMB