California Dreamin’ of Reliable Power
Californians have recently been enduring rotating blackouts – short term loss of power due to excessive demand. When the lights go out and the a/c units no longer hum, it’s always political. Oddly, both sides can agree that climate change is to blame. Liberals attribute the extended high temperatures in southern California to the gradual manmade warming that is afflicting the planet. Conservatives see a reliance on unreliable renewables as the cause – underlying the power supply shortfall was the loss of 100MW of output from a wind farm.
Perhaps global warming is making it less windy. Environmental extremists will argue that fighting climate change is ever more urgent, while pragmatists will note that using more intermittent renewables is leaving consumers vulnerable to shortages.
What’s happening in California is important to all Americans, because it’s a preview of what an energy policy run by environmental extremists could look like if inflicted across the entire country.
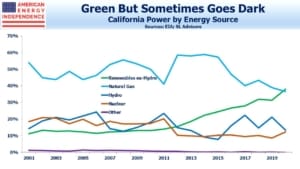
For the past decade, California has been steadily pushing renewables’ share of power generation. For much of that time natural gas was easily the biggest source of electricity, since coal use stopped completely in 2015.
But environmental extremists have been single-minded in their desire to run everything with solar panels and windmills. Although the state has not banned natural gas, it does allow cities and counties within the state to do so. Diablo Canyon, California’s last remaining nuclear power plant, will close its two reactors in 2024-25.
In 2018, California passed a law mandating 50% of its electricity to be from renewable sources by 2025, 60% by 2030 and 100% by 2045. There are no plans to build new nuclear capacity, so it looks like sun and wind will be the major source of power.
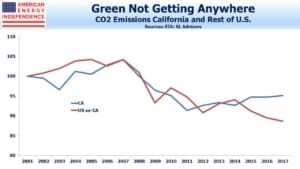
America has been reducing its CO2 emissions, but oddly California has been lagging the rest of the country, with a slight worsening since 2011. This fact must sit uncomfortably with those thoughtful advocates of California as a leader in renewables. The problem, as anyone trying to drive around Los Angeles knows, is that transportation still relies heavily on fossil fuels. A couple of years ago when I was visiting clients with a salesperson for a couple of days, traffic estimates were critical to our meeting schedule. In fact, every meeting seemed to open with a brief chat about the 405. Automobiles and traffic jams generate a lot of California’s emissions.
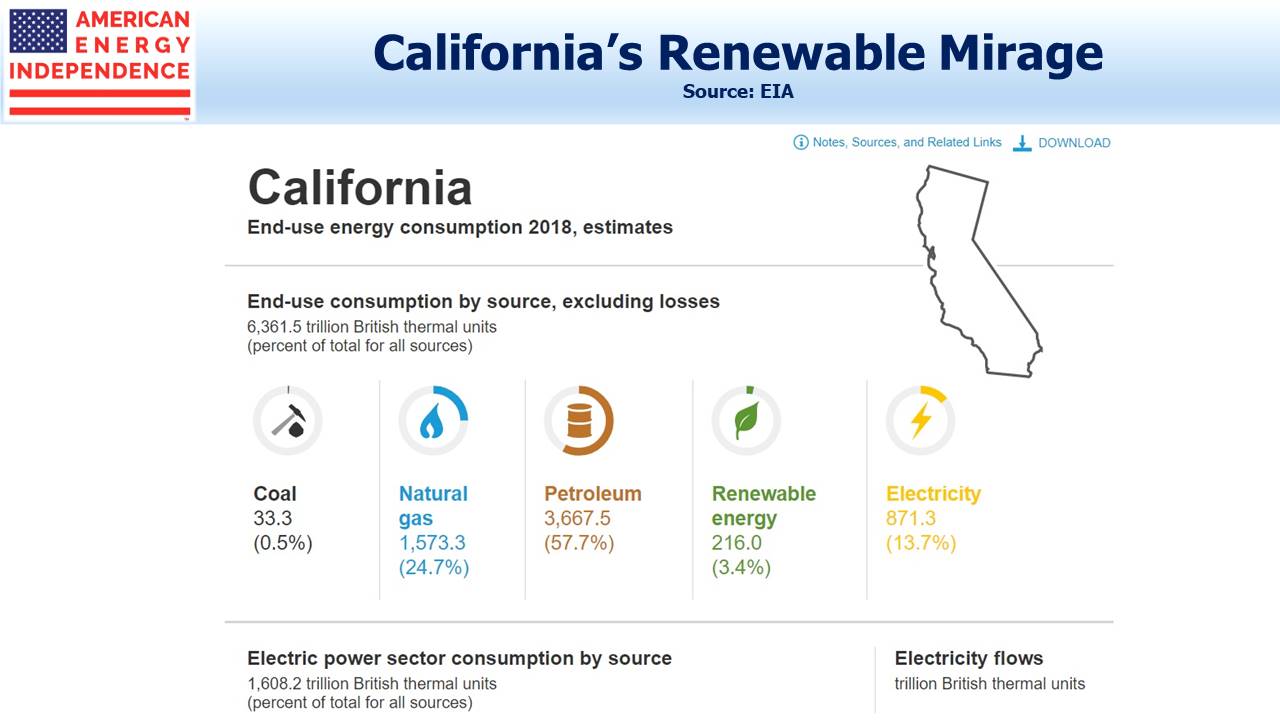
California’s renewables effort has focused on electricity, but that’s less than 14% of total energy consumption. This is why the popular image of green California isn’t reflected in reduced emissions.
The average retail price of electricity in California is 16.58 cents, versus 10.53 cents for the country as a whole. Unreliable power that costs 57% more than the average, along with a slower rate of emissions reduction, are not the hallmarks of a successful policy to combat climate change. This is where the drivers of Joe Biden’s energy policy are hoping to take us. The Biden-Sanders Unity Task Force has recommended, “…eliminating carbon pollution from power plants by 2035”. This is a decade ahead of California – because it’s going so well there.
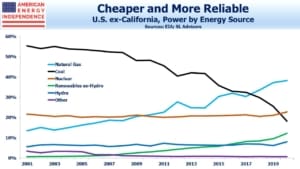
California’s power blackouts are in part because the wind has inconveniently not been blowing when needed. This is why natural gas is such a good compliment to intermittent renewables – it’s always available. Many other U.S. states have embraced this, including Nextera (NEE), loved by environmentalists and investing in natural gas pipelines.
Energy density is another challenge that will lead to NIMBY problems.
An article in the Financial Times (see Green power needs to be dense power) compared the 950 acres required for a UK solar farm to produce 350 megawatts of power with the 80 acres to house a nuclear project with 3,200MW of output. Not only is this 9X the power output on under 9% of the land, but the solar plant is only expected to operate at 11% capacity, versus 90% for the nuclear. The power output per acre is 1,000 times lower for this solar installation compared with nuclear, a significant problem in densely populated Britain.
Any solar installation in the UK is a green extremist triumph in willful denial of the climate – but at least they’re still building nuclear plants, because they do want to keep the lights on.
California’s blackouts show what happens when climate extremists run energy policy. The silver lining for investors is that such policies lead to, and desire, high energy prices – both as a constraint on demand and also because it makes renewables less uncompetitive. Returns on energy investments tend to follow energy prices. Green policies that constrain supply need not be bad for the sector.
We are invested in all the components of the American Energy Independence Index via the ETF that seeks to track its performance.